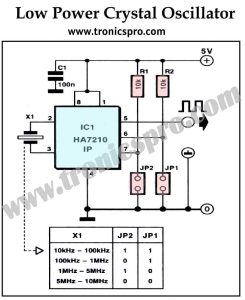
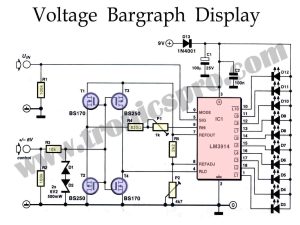
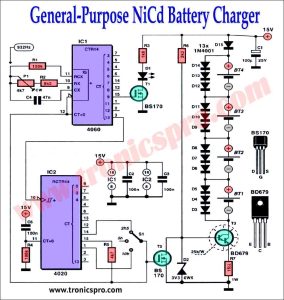
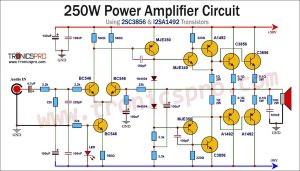
Introduction
Lead acid batteries are commonly used in a wide range of applications, and they require protection circuits that can prevent overcharging and over-discharging. Failure to protect lead-acid batteries properly can lead to degraded performance, reduced lifespan, and even fire hazards. In this article, we will discuss the use of the LM10C and BD139 transistor in designing a Lead Acid Battery Protector circuit that can monitor the battery voltage and prevent overcharging and over-discharging.
Circuit Diagram of Lead Acid Battery Protector
The Lead Acid Battery Protector can be designed using a few basic components. The circuit diagram of this project is shown below.
More Circuit Layouts

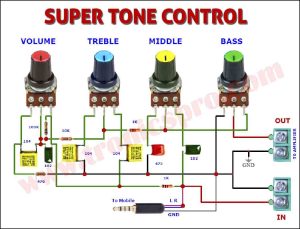



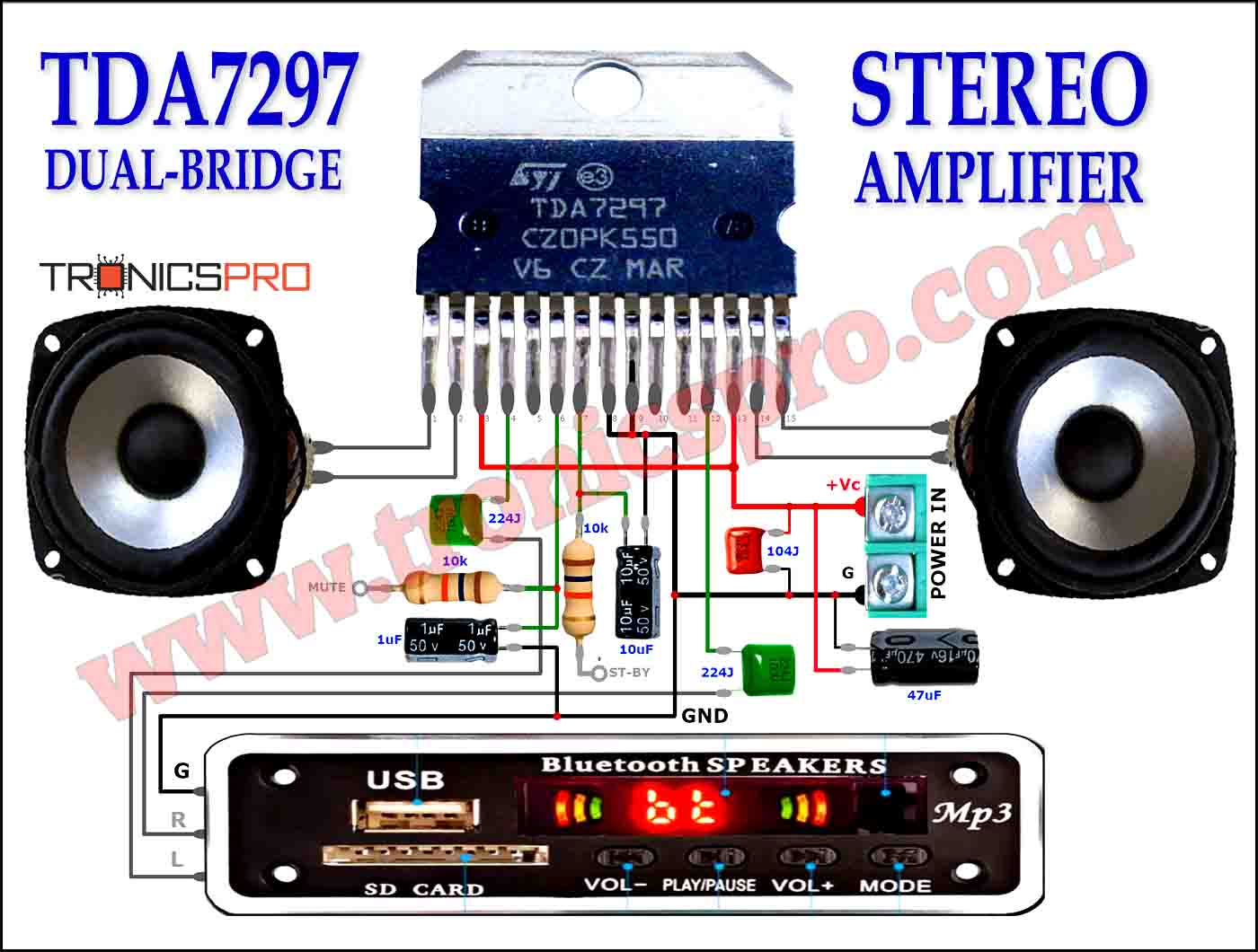

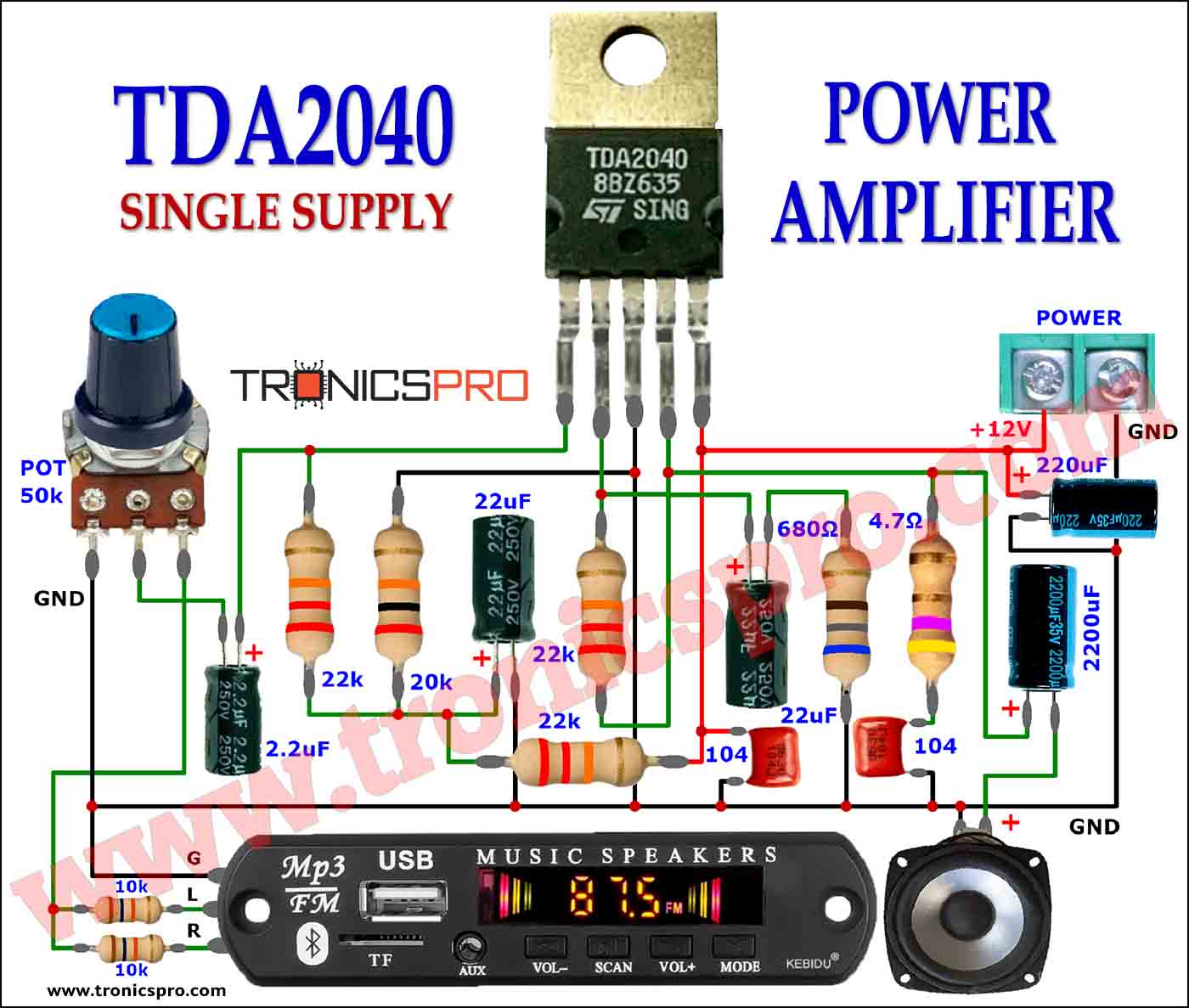

Explanation of Lead Acid Battery Protector
LM10C IC:
The LM10C is a precision voltage reference chip that can be used to provide accurate voltage measurements for various applications. It has a low voltage tolerance of +/- 1%, making it an ideal component for battery protection circuits.
The LM10C can operate at a wide range of voltages from 1.2V to 40V, and it consumes very low power, making it suitable for portable and low-power applications. It also has a high input impedance, which makes it easy to interface with other components.
BD139 Transistor:
The BD139 transistor is an NPN bipolar junction transistor that can be used in a wide range of applications, including as a switch and amplifier. It has a maximum collector current of 1.5A and can handle a maximum voltage of 80V.
The BD139 transistor is commonly used in battery protection circuits as a switch that can turn on or off the charging or discharging currents. It also has a high gain and low saturation voltage, which makes it suitable for driving other components.
Lead-Acid Battery Protector :
The lead-acid battery protector circuit using the LM10C and BD139 transistor is a simple and effective way to prevent overcharging and over-discharging of lead-acid batteries. The circuit consists of two parts: the voltage sensing and the switching parts.
Voltage Sensing:
The voltage sensing part of the circuit consists of the LM10C and two resistors. The LM10C is configured as a voltage divider, with one resistor connected between its VOUT pin and ground, and the other resistor connected between the battery positive terminal and the VOUT pin.
The voltage across the battery terminals is divided by the two resistors and fed into the LM10C, which generates a reference voltage. The output voltage of the LM10C is compared to the reference voltage using a comparator to determine the battery state.
Switching:
The switching part of the circuit consists of the BD139 transistor and a relay. The relay is connected between the battery positive terminal and the charging/discharging circuit. The BD139 transistor is used as a switch to turn on or off the relay.
When the battery voltage is above a certain threshold, the output of the comparator turns on the BD139 transistor, which activates the relay and allows the charging current to flow into the battery. When the battery voltage drops below a certain threshold, the output of the comparator turns off the BD139 transistor, which deactivates the relay and prevents the battery from over-discharging.
Conclusion of Lead Acid Battery Protector :
Lead acid batteries require proper protection circuits to prevent overcharging and over-discharging, which can degrade performance and shorten the lifespan of the battery. The LM10C and BD139 transistor are two important components that can be used to design an effective and simple lead acid battery protector.
By sensing the battery voltage and switching the charging/discharging current using a relay and BD139 transistor, the lprotector can prevent damage to the battery and improve its lifespan.
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- 12V-220V H-Bridge Inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- 18650 battery bank free charge protection module
- D718 B688 Bass Amplifier Homemade DIY
- C5200 Bass Amplifier DIY Homemade with Volume
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
- C5200 A1943 TDA2030 Amplifier DIY Homemade