Introduction
In the realm of modern electronics, seamless and uninterrupted power supply is crucial for the efficient operation of various devices and systems. Automatic Battery Switch Over circuits have become indispensable solutions, ensuring a smooth transition from one power source to another. In this article, we will explore a circuit diagram that employs the BRX49 SC, BC557 Transistor, and 1N4001 Diode to facilitate a reliable battery switch-over mechanism. These components, known for their high-performance capabilities, come together to create an efficient and dependable circuit for managing power backup systems.
The circuit as shown below, is designed for a 6 V battery system using rechargeable batteries. It provides automatic switch over to a charged reserve battery when the voltage of the main battery approaches the fully discharged level. The clever thing about this circuit is that the actual switch over of the battery is voltage-dependent and is adjustable, even though this circuit essentially consists of only two components. The active element is a small SCR (type BRX49), which is connected between the load and the reserve battery. For calibrating the switch over point, an incandescent lamp is connected as a load. In actual use, however, the load can be anything having a maximum current consumption of 300 mA at about 5 V.
The cathode of the SCR is connected to the load, with the anode connected to the positive terminal of the reserve battery. The gate of the SCR is also connected to the positive terminal of the reserve battery via a 47-k trimpot (P1).
Circuit Diagram of Automatic Battery Switch Over
This project can be designed using a few basic components. The circuit diagram of this project is shown below.
More Circuit Layouts

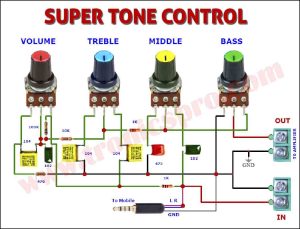



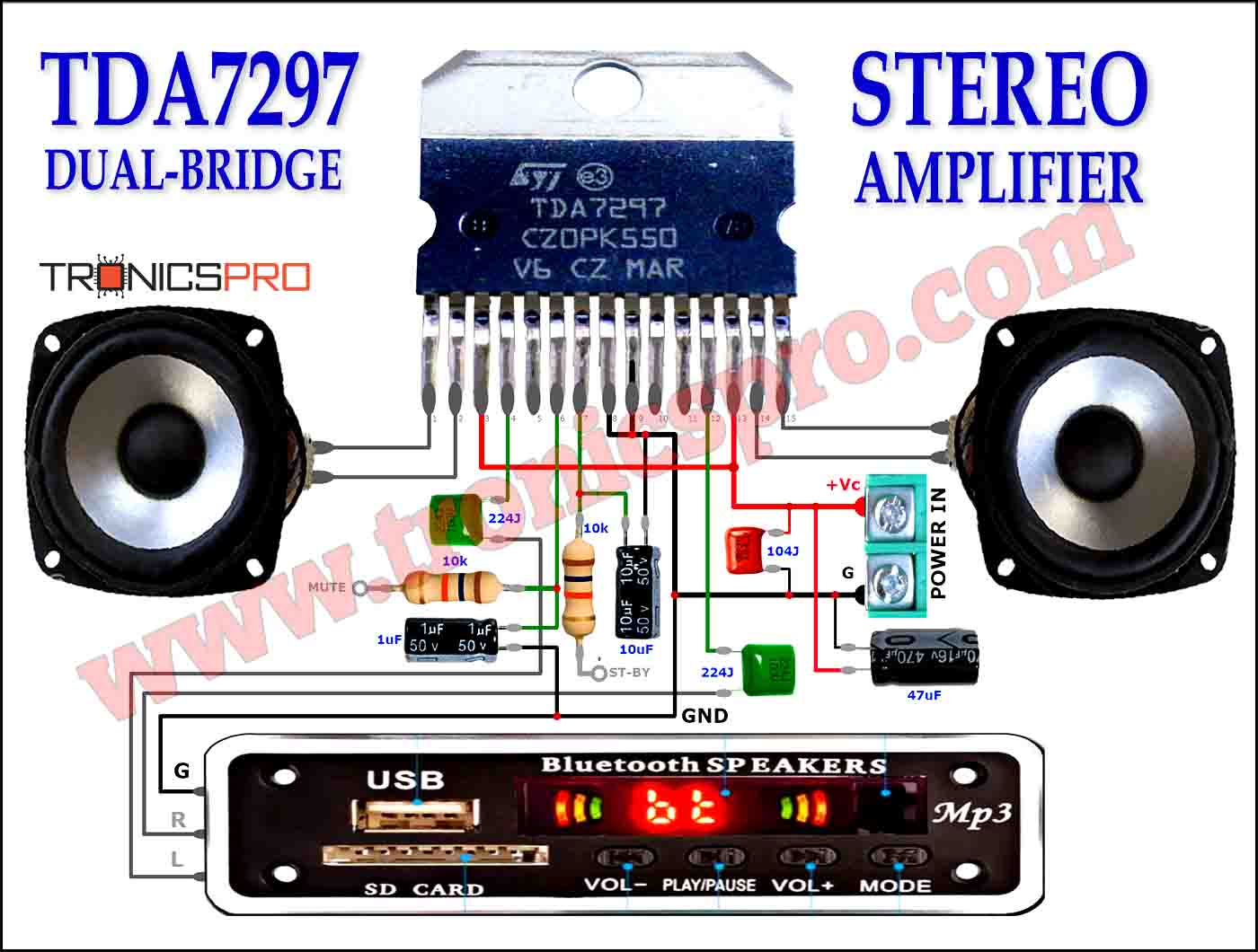

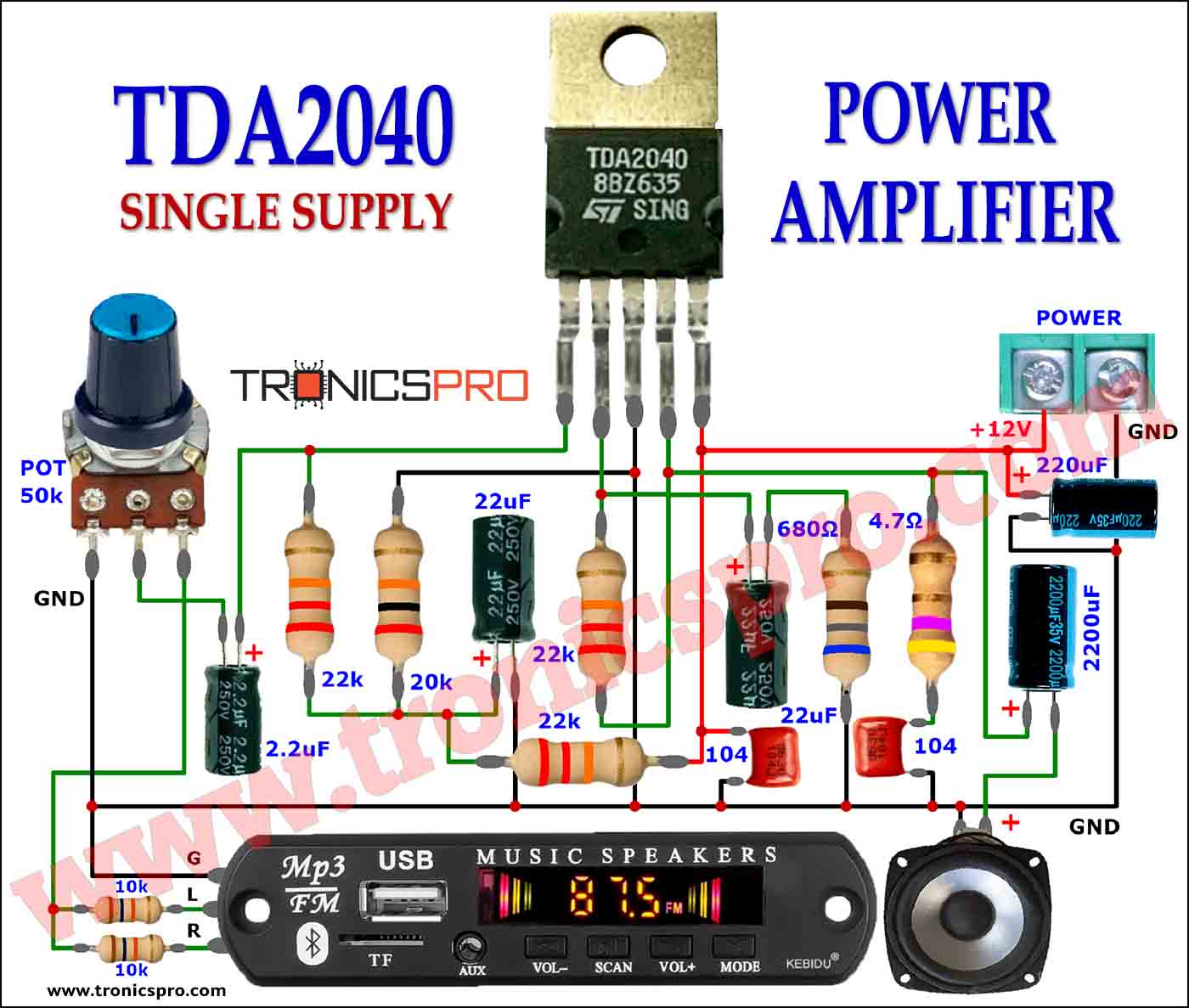
Components List of Automatic Battery Switch Over
Following is the list of all components used in this project:
- BC557 Transister x 1
- 1N4001 Diode x 1
- BRX49 SCR (silicon-controlled rectifier) x 1
- 47k Variable Resister x 1
- 270 Ohms Resister x 1
- 680 Ohms Resister x 1
- LED Light x 1
- Load Lamp 5V, 0.3A x 1
Working Explanation of Automatic Battery Switch Over
This already clearly suggests how the automatic switch over works. The voltage across the SCR is the difference between the two battery voltages. Initially, with both batteries fully charged, the voltages of the two batteries are nearly the same. The SCR is thus cut off, since there is not any significant voltage across it and no gate current flows via P1. As the main battery becomes increasingly discharged, the voltage across the load decreases, which means that the voltage at the cathode of the SCR decreases. The anode becomes positive with respect to the cathode and the gate. A gate current starts to flow via P1, with the magnitude depending on the voltage and the value of P1. As soon as the gate current exceeds the triggering threshold of the SCR, the SCR fires (which means that it suddenly starts to conduct) causing the reserve to be connected to the load. Since the voltage of the reserve battery is higher than that of the discharged main battery, diode D1 is cut off, preventing any current from flowing from the reserve battery into the main battery.
Diode D1 not only prevents a reverse current flow from the reserve battery into the main battery, it also forms the part of an indicator circuit in combination with transistor T1 and LED D2. As long as a current flows from the main battery through D1, a base current also flows through the base-emitter junction of the transistor, which, together with base resistor R1 is connected in parallel with D1. This causes the transistor to conduct, so LED D2 is illuminated to indicate that the main battery is in use. When the circuit switches over to the reserve battery, T1 is also cut off, and the LED is immediately extinguished.
To calibrate the circuit, connect only the reserve battery to the circuit (a non-rechargeable battery can also be used), and replace the mains battery by an adjustable power supply whose output voltage can be varied over (at least) the range of 5 V to 8 V. After first setting P1 to maximum resistance, adjust the power supply voltage to approximately 5.3 V, and then slowly rotate the trimpot until the switch over occurs which can be recognized by the LED going out. Next, increase the power supply voltage and then reduce it again, in order to verify the operation of the circuit.
If necessary, the setting of the trimpot should be readjusted until switch over occurs reliably when the desired voltage is present at the main battery terminal.
Introduction to Major Components
BRX49 SC:
The BRX49 SC is a silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) with outstanding switching capabilities. SCRs, also known as thyristors, are semiconductor devices that can control the flow of electric current. The BRX49 SC exhibits high surge current and voltage ratings, making it ideal for applications that demand robust and reliable switching. Its excellent sensitivity to trigger signals ensures swift activation, enabling the Automatic Battery Switch Over circuit to swiftly respond to changes in the primary power source’s status. With its exceptional ability to handle high currents and voltages, the BRX49 SC is a key component in the battery switch-over circuit, enhancing its efficiency and overall performance.
BC557 Transistor:
The BC557 is a PNP (positive-negative-positive) bipolar junction transistor (BJT) renowned for its versatility and application in various electronic circuits. It is a low-power transistor, capable of handling moderate current and voltage levels. When used in the Automatic Battery Switch Over circuit, the BC557 transistor serves as a reliable switch to control the path of current between different power sources. Its low saturation voltage minimizes power losses, ensuring efficient energy transfer within the circuit. The BC557’s small form factor and compatibility with different signal types make it an excellent choice for the automatic battery switch-over mechanism, contributing to the circuit’s overall stability and performance.
1N4001 Diode:
The 1N4001 is a standard power rectifier diode, designed to efficiently conduct current in one direction while impeding the flow in the opposite direction. As a general-purpose diode with a high forward current rating and low reverse leakage, the 1N4001 is widely used in various electronic circuits, including the Automatic Battery Switch Over circuit. By strategically placing the 1N4001 diode in the circuit, it ensures the unidirectional flow of current, preventing any undesired backflow of power and thereby protecting sensitive components. Its fast response time and robust construction enhance the overall reliability and safety of the battery switch-over circuit.
Conclusion of Automatic Battery Switch Over
In conclusion, the Automatic Battery Switch Over circuit diagram featuring the BRX49 SC, BC557 Transistor, and 1N4001 Diode exemplifies the seamless integration of high-performance components to achieve uninterrupted power supply. The BRX49 SC brings its exceptional switching capabilities to the table, allowing for swift and efficient response to power source changes. The BC557 Transistor acts as a reliable switch, controlling the current path between power sources with minimal power losses. Additionally, the 1N4001 Diode ensures the unidirectional flow of current, enhancing circuit safety and stability. By synergistically combining these components, the Automatic Battery Switch Over circuit ensures continuous operation of electronic systems, making it an indispensable asset in power management applications.
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- 12V-220V H-Bridge Inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- 18650 battery bank free charge protection module
- D718 B688 Bass Amplifier Homemade DIY
- C5200 Bass Amplifier DIY Homemade with Volume
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
- C5200 A1943 TDA2030 Amplifier DIY Homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.