The 2N4126 pinout follows the Emitter–Base–Collector (E–B–C) sequence, and it is a PNP silicon transistor designed for low-power amplification and signal switching in general electronic circuits. With a collector–emitter voltage (Vce) of 25V, collector–base voltage (Vcb) of 25V, collector current (Ic) up to 200mA, and power dissipation of 650mW, the 2N4126 transistor is widely used in audio preamplifier, oscillator, and low-frequency driver circuits.

Introduction to 2N4126 PNP Transistor
The 2N4126 PNP transistor is a silicon small-signal device housed in a TO-92 plastic package, built for reliable performance in low-voltage circuits. It is mainly used where low noise, moderate gain, and fast response are required — such as in analog amplifiers, switching circuits, and frequency oscillators.
Thanks to its compact design, 2N4126 transistor serves as an excellent component for compact audio and sensor control boards. When paired with its complementary NPN transistor 2N4124, it offers excellent symmetry, linearity, and temperature stability in amplifier circuits.
2N4126 PNP Transistor

Pinout of 2N4126

Understanding the 2N4126 Pinout Configuration
The 2N4126 pinout uses a simple Emitter–Base–Collector (E–B–C) arrangement when viewed from the flat face of the TO-92 package. This configuration makes it easy to use on breadboards and PCBs.
Pin Configuration of 2N4126 Pinout
| Pin# | Pin Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter |
| 2 | Base |
| 3 | Collector |
Key Features of 2N4126 Transistor
- Small-signal PNP silicon transistor for general use
- Designed for low-power amplification and switching
- Low noise operation for clean audio output
- Fast switching response for digital control
- Compact TO-92 package suitable for PCB mounting
- Complementary with 2N4124 NPN transistor
2N4126 Transistor Datasheet and Specifications
- Collector–Emitter Voltage (Vce): 25V
- Collector–Base Voltage (Vcb): 25V
- Emitter–Base Voltage (Veb): 5V
- Collector Current (Ic): 200mA
- Total Power Dissipation (Pc): 650mW
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 50 to 250
- Transition Frequency (fT): 200MHz (typical)
- Package Type: TO-92
- Polarity Type: PNP
- Pin Configuration: Emitter–Base–Collector (E–B–C)
Working Principle of 2N4126 Transistor
The 2N4126 PNP transistor functions by allowing current flow from emitter to collector when its base is at a lower potential. A small base current controls a much larger collector current, enabling it to act as both a switch and an amplifier.
When used in switching applications, applying a negative voltage to the base relative to the emitter turns the transistor on, allowing current conduction. In amplifier circuits, small variations in base current cause proportional changes in collector current, achieving signal amplification.
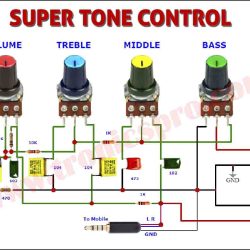
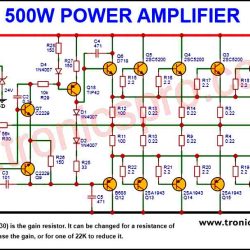
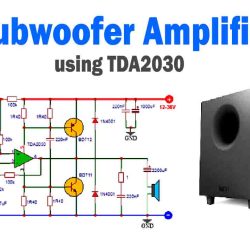
More Circuit Layouts
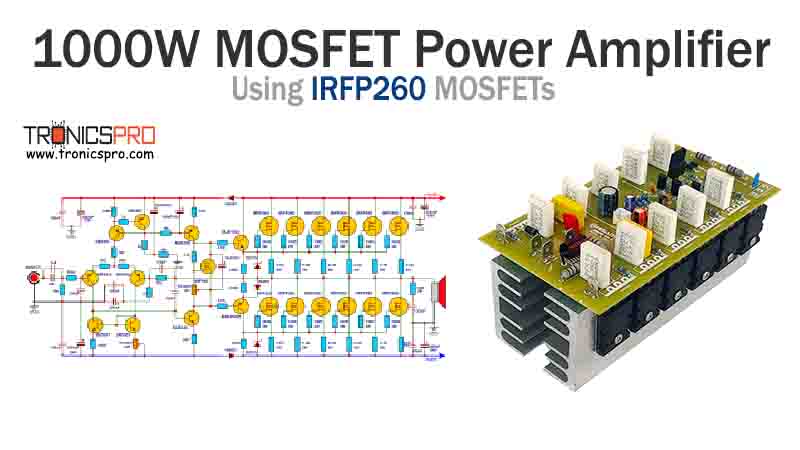
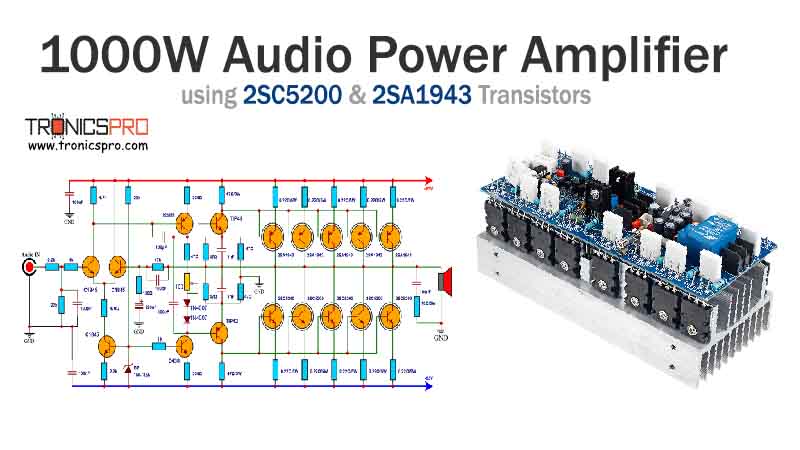
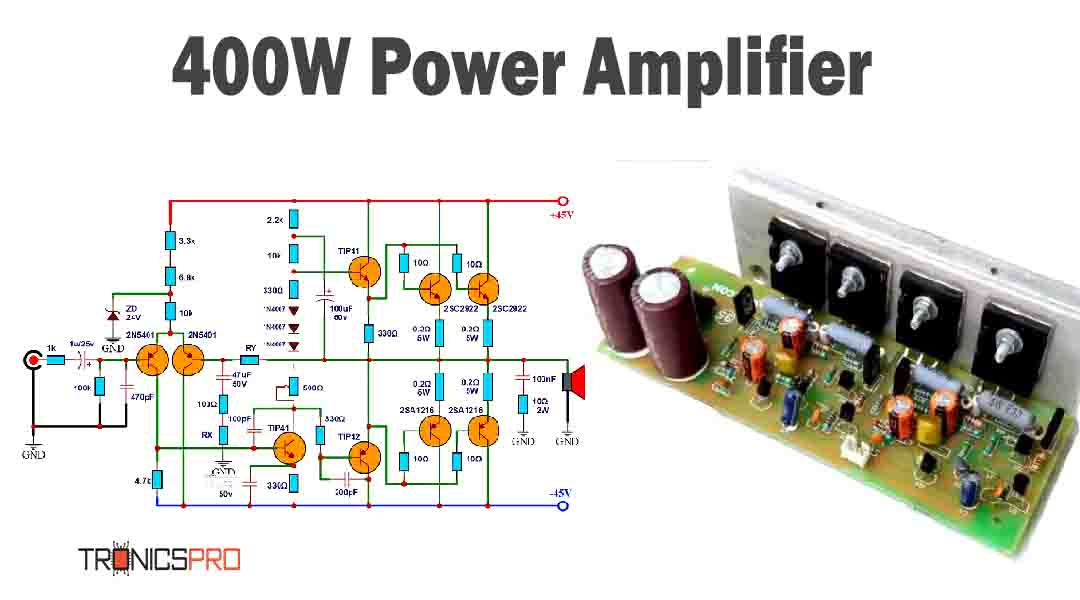
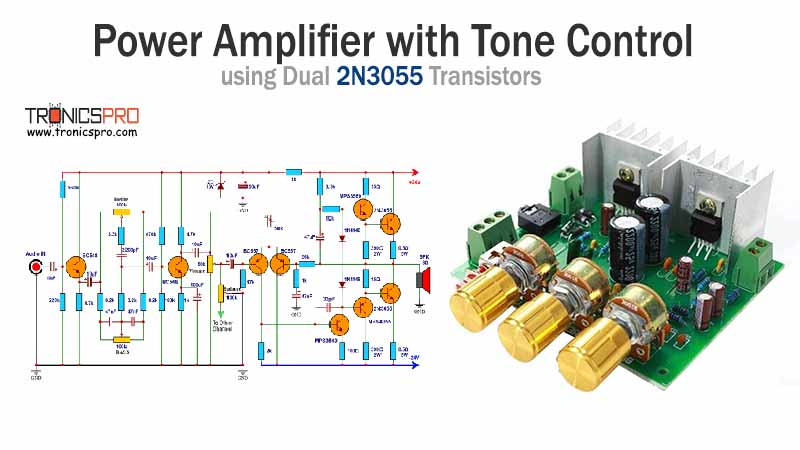

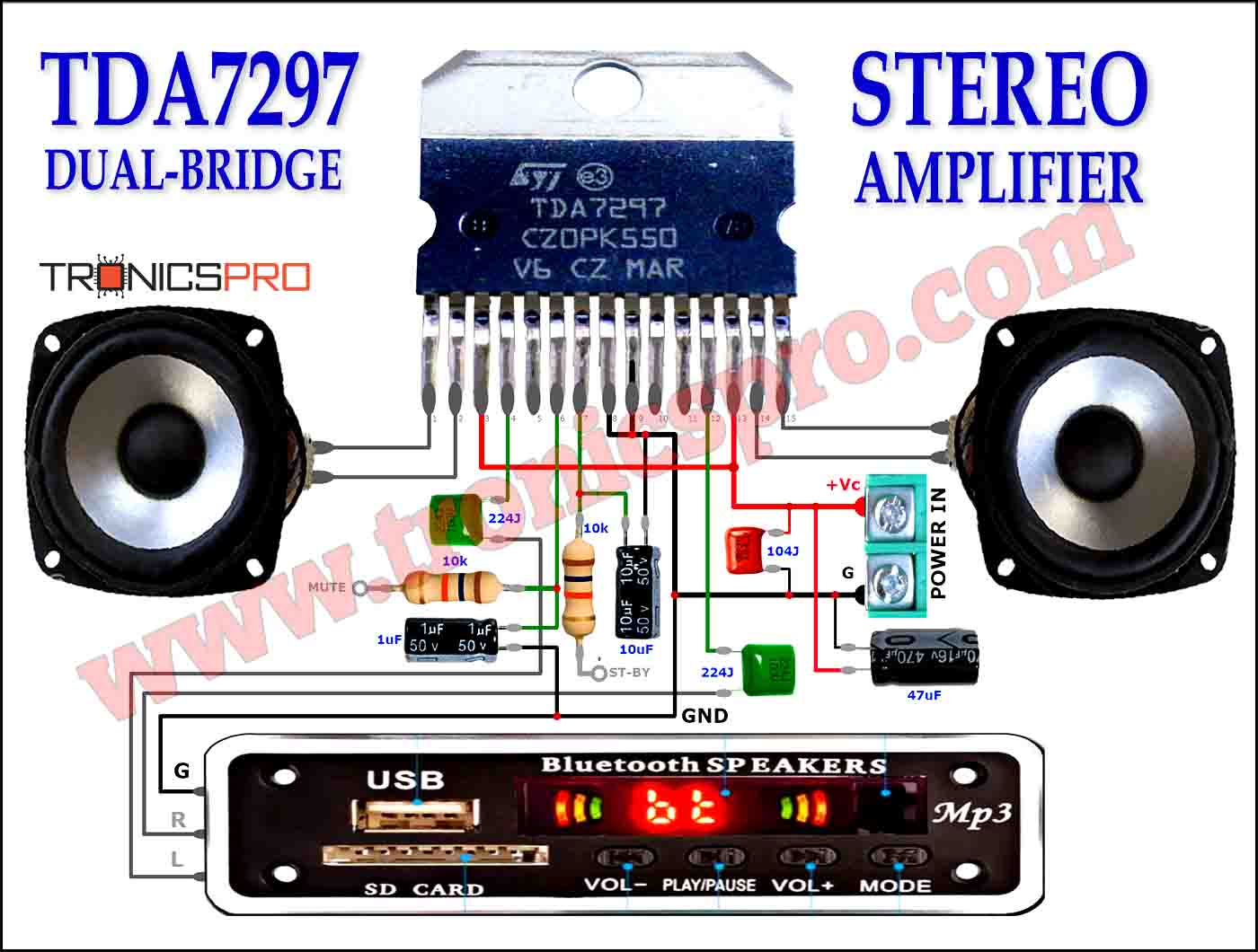

Typical Applications of 2N4126
- Audio signal preamplifiers and low-frequency amplifiers
- Analog switching and signal processing circuits
- Complementary amplifier pairs with 2N4124 NPN
- Multivibrator, oscillator, and waveform generator circuits
- General-purpose switching in control and logic circuits
- Sensor interface and driver circuits
NPN Complementary Transistor
The 2N4124 NPN transistor is the complementary pair to the 2N4126 PNP transistor. Both devices share the same voltage and current ratings but differ in polarity. This makes them suitable for push-pull output stages, balanced amplifier circuits, and signal driver circuits where complementary operation is required.
Equivalent Transistors and Alternatives
- 2N3906 – General-purpose PNP transistor
- BC557 – Low-noise small-signal transistor
- 2N4403 – Medium-current PNP transistor
- PN2907A – Common-use amplifier transistor
- S9015 – PNP transistor for low-voltage applications
Comparison Summary: 2N4126 vs 2N4124
The 2N4126 (PNP) and 2N4124 (NPN) transistors form a complementary pair with identical voltage, current, and power ratings. The only difference lies in their polarity and direction of current flow.
The 2N4126 transistor conducts when the base is more negative than the emitter, while the 2N4124 transistor conducts when the base is more positive. This opposite polarity relationship makes the pair perfect for push-pull amplifier configurations, delivering symmetrical output and low distortion in signal amplification.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the maximum collector current of 2N4126?
It supports a maximum collector current of 200mA, suitable for signal and low-current applications.
Can 2N4126 be used for amplification?
Yes, the 2N4126 PNP transistor is ideal for audio, signal, and oscillator amplification.
What is the 2N4126 pin configuration?
The 2N4126 pinout is Emitter–Base–Collector (E–B–C) from left to right when the flat side faces you.
What is the complementary transistor for 2N4126?
The 2N4124 NPN transistor is its complementary device, sharing the same electrical parameters.
What is the power dissipation of 2N4126?
The total power dissipation is 650mW, ideal for low-power circuit designs.
Conclusion
The 2N4126 PNP transistor is a compact, reliable component for low-power amplification and signal control. Its 25V collector-emitter voltage, 200mA current capacity, and 650mW power rating make it a suitable choice for analog, switching, and complementary amplifier circuits.
When combined with the 2N4124 NPN transistor, it provides excellent balance, low distortion, and high efficiency in push-pull amplifier designs and driver circuits, maintaining stable performance across a wide frequency range.
Datasheet & Pinout of 2N4126 NPN Transistor
Click the following Button to download the datasheet of 2N4126 Transistor :
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.