Introduction
Power amplifier circuits are essential components of audio systems, enabling them to produce clear and loud sound. One widely used combination in power amplifier circuits is the C5200 and A1943 transistors. These transistors are well-regarded for their excellent performance and reliability. This article will provide a detailed insight into the power amplifier circuit diagram using C5200 and A1943 transistors, along with separate specifications of these transistors and other relevant components.
Component Specifications
2SC5200 Transistor:
The C5200 is a silicon NPN power transistor that operates at a maximum voltage of 230V and dissipates up to 150W. It has a collector current (Ic) rating of 15A, making it suitable for high-power applications. The transistor is housed in a TO-264 package, which ensures efficient heat dissipation. The C5200 offers low saturation voltage, high current gain, and excellent linearity, contributing to its superior performance as a power amplifier component.
2SA1943 Transistor:
The A1943 is a complementary PNP transistor to the C5200, making it ideal for use in push-pull amplifier configurations. It also operates at a maximum voltage of 230V and dissipates up to 150W. The A1943 has a collector current rating of 15A, providing ample current handling capability. Like the C5200, the A1943 is housed in a TO-264 package, ensuring effective heat dissipation. Its low saturation voltage and high current gain make the A1943 a reliable choice for power amplifier applications.
2N5551 Transistor:
The 2N5551 transistor is a complementary PNP transistor to the 2N5401 transistor. It operates at a maximum voltage of 150V and dissipates up to 0.625W. The 2N5551 has a collector current rating of 0.5A, making it suitable for low to medium power applications. This transistor is housed in a TO-92 package, which is widely used for small signal transistors due to its compact size and cost-effectiveness. Its high current gain and excellent switching characteristics make the 2N5551 an excellent choice for various audio amplifier applications.
2N5401 Transistor:
The 2N5401 transistor is a complementary NPN transistor to the 2N5551 transistor. It operates at a maximum voltage of 150V and dissipates up to 0.625W. The 2N5401 has a collector current rating of 0.6A, suitable for low to medium power applications. It is also housed in a TO-92 package, allowing for easy integration into small signal circuits. The 2N5401 offers low saturation voltage and high current gain, making it suitable for audio amplifier applications.
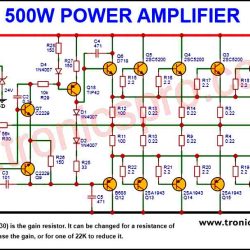
Circuit Diagram of Power Amplifier Circuit C5200 A1943
This project can be designed using a few basic components. The circuit diagram of this project is shown below.

More Circuit Layouts

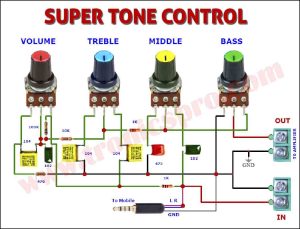



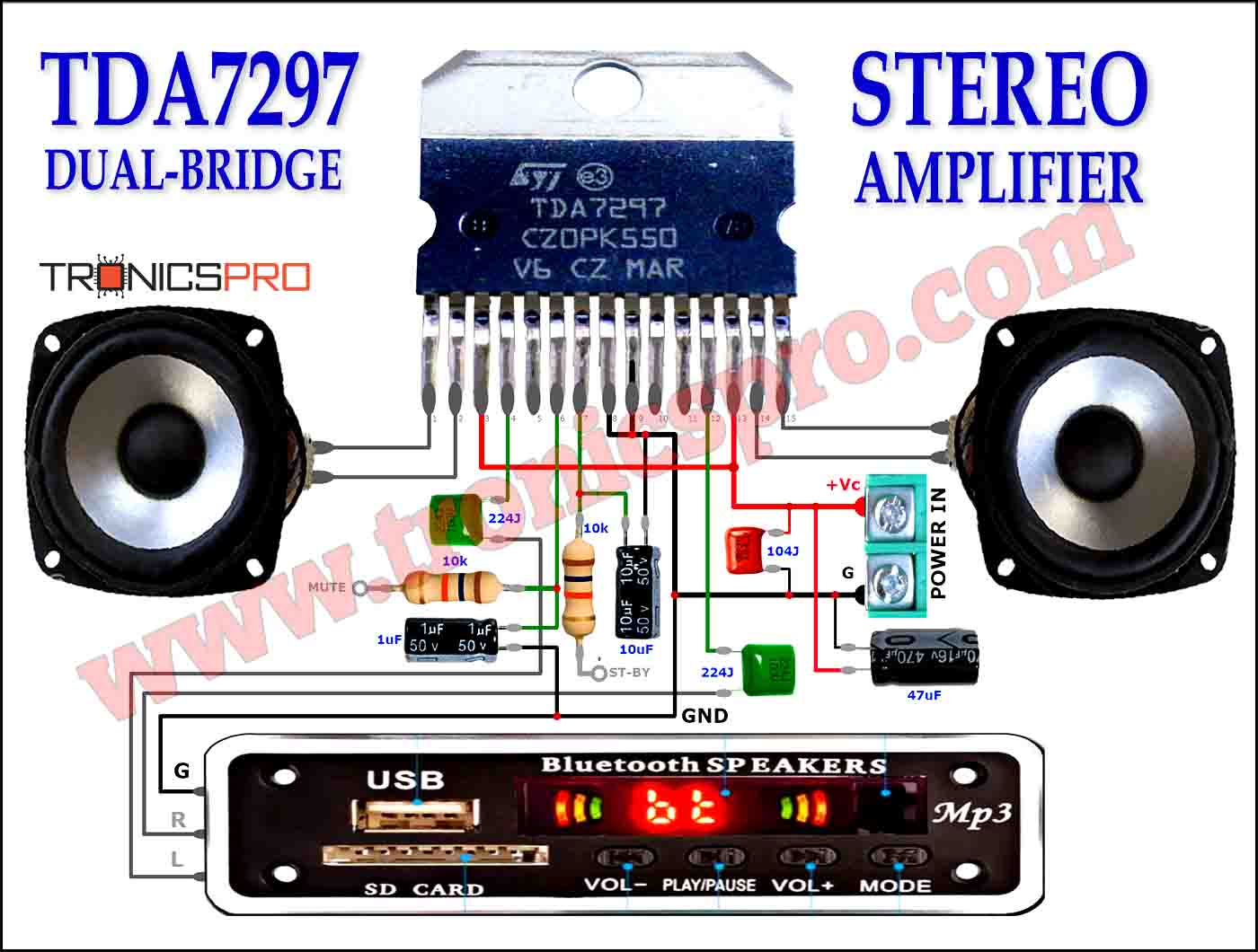

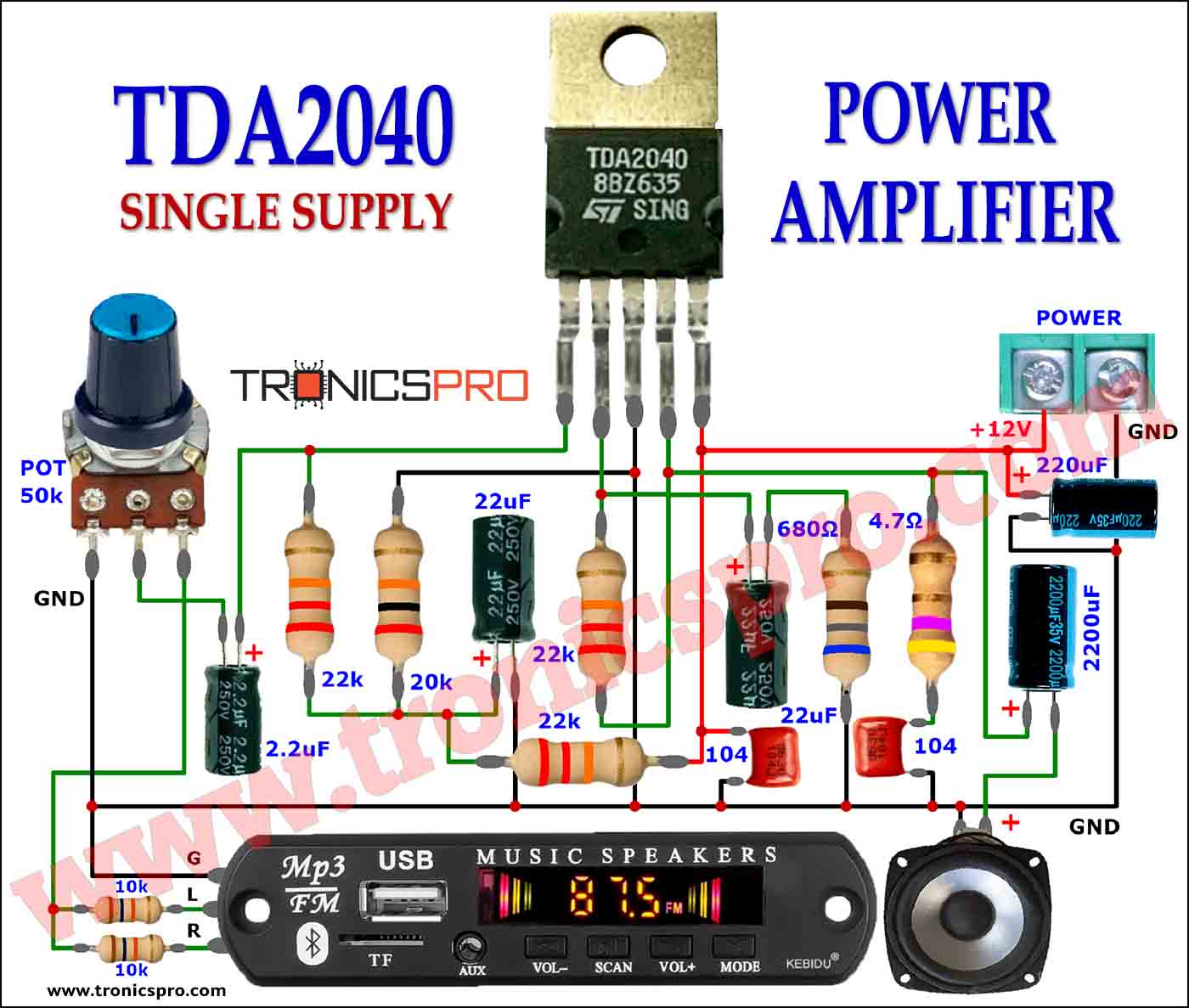
Components List of Power Amplifier Circuit C5200 A1943
Following is the list of all components used in this project:
- 2SC5200 Transistor x 1
- 2SA1943 Transistor x 1
- 2N5551 Transistor x 2
- 2N5401 Transistor x 3
- 0.22 ohms 5W Resister x 2
- 10 ohms Resister x 1
- 2.2k Resister x 1
- 100k Resister x 1
- 4.7k Resister x 2
- 47k Resister x 2
- 1k Resister x 1
- 100uF Capacitor x 1
- 1uF Capacitor x 2
- 1N4148 Diode x 2
Working Explanation of Power Amplifier Circuit C5200 A1943
The power amplifier circuit diagram using C5200 and A1943 transistors is a class AB amplifier that operates with ±40VDC symmetrical voltage. This circuit can deliver an output power of approximately 100W, providing sufficient power for most audio applications.
The input section of the circuit consists of a voltage divider network that acts as a biasing circuit for the transistors. This network is formed by resistors. Capacitor provides AC coupling, allowing the input audio signal to pass through while blocking the DC component. The input signal is then amplified by transistor, which operates in the common-emitter configuration.
The amplified signal from the base of transistor is fed to the bases of power transistors C5200 and A1943. These transistors are responsible for delivering the required power to the output stage of the amplifier. The output stage coupled to the speakers, which converts the electrical signal into sound energy.
The power supply section of the circuit is crucial for providing stable and clean DC voltage to the amplifier. It consists of a bridge rectifier circuit that converts the 220VAC mains voltage to DC voltage. Capacitor filters out any remaining AC ripples from the rectified voltage, resulting in a clean DC output. The regulated DC voltage is then applied to the amplifier circuit.
Conclusion:
The power amplifier circuit using C5200 and A1943 transistors provides a reliable and efficient solution for audio power amplification. These transistors, along with the additional components discussed, contribute to the excellent performance and stability of the amplifier. By understanding the specifications of the C5200, A1943, 2B5551, and 2N5401 transistors, designers can make informed decisions while selecting components for their amplifier circuits. Whether it is for home audio systems, professional sound systems, or any other audio
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- 12V-220V H-Bridge Inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- 18650 battery bank free charge protection module
- D718 B688 Bass Amplifier Homemade DIY
- C5200 Bass Amplifier DIY Homemade with Volume
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
- C5200 A1943 TDA2030 Amplifier DIY Homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.























I need the circuit diagram for Toa amplifier modelA 1120A or something similar to the Toa A 1120A