Introduction
If you love playing bass, having an introduction bass amplifier for surround sound can really amp up your sound. These reliable amps are capable of producing loud, clean tones and dynamic punch while maintaining the natural tone characteristics of your instrument. They provide a long-lasting solution to powering up because they’re equipped with advanced power sections that generate enough headroom for even tough live performances. Plus, many models have multiple channels and adjustable parameters that allow you to customize your sound to fit the style. Whether you are a beginner or a professional bass player, investing in one of these amplifiers is sure to take your sound to the next level.
What is a Bass Amplifier?
A bass amplifier is essential for any bass player and takes your sound to the next level. It works by increasing the low frequencies of your instrument to create a sound unique only to the bass, which maintains clarity and eliminates any distortion that could otherwise occur when playing live. The amp also includes features such as adjustable treble, saturation, and even overdrive to give you complete control over your sound. Additionally, most amps come with an EQ setting so you can further personalize and shape your tone as desired. With its increased power output, superior audio fidelity, and customizable capabilities, a bass amplifier is a must-have for any serious musician looking to get their sound just right.
Benefits of a Bass Amplifier for Surround Sound:
A bass amplifier is an essential part of any surround sound setup. It ensures that when listening to your favorite movie or music, you hear all the low-end frequencies which give it its fullness and richness. The benefits of this vary from simply adding more dimension to a track, to improving the quality of sound, and immersing the listener in their audio experience. The right amplifier will also allow you to customize your system with features such as adjustable crossover and phase control, allowing you to fine-tune your sound experience. Bass amplifiers are also great for adding extra power to a system, enabling it to get that deep satisfying thump across larger rooms with ease. So if you’re looking for an amazing way to bring surround sound into your home, investing in a good quality bass amp is well worth considering.
Features to Look for in a Bass Amplifier:
When selecting a bass amplifier, there are a few features to consider. First, look for an amp with plenty of wattage and power. More wattage equals more volume, so it’s essential that your amp can provide the headroom you need for larger venues or practice spaces. Additionally, many amps have built-in effects such as delay or chorus to enhance the sound of your bass. Various models also offer specialized EQ settings to help you tweak your tone in different environments. If portability is important to you, look for lightweight amps with built-in handles or straps. Finally, make sure that you’re looking into pricing and warranties before you make your purchase so that you’re sure to get the best value out of your investment.
How to Choose the Right Bass Amplifier:
When it comes to choosing the right bass amplifier, it’s important to consider your needs. Start by thinking about where and how you’ll be playing – in a large venue, at home, or on the road. Once you know what size venue you’ll be playing in, think about the type of sound you need – warm and round for jazz or darker and punchy for punk rock. What other features will you need from an amp like onboard effects or reverb dials? Don’t forget to take into account your budget as larger amplifiers can get expensive. Visit a local music store and try out different models to compare the variations so that you make sure you choose the one that fits best with your goals.
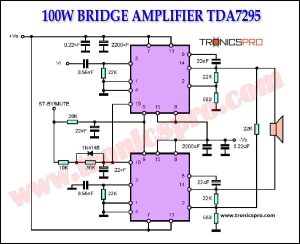
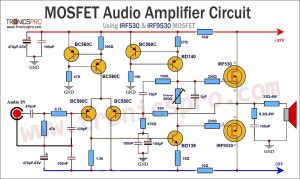
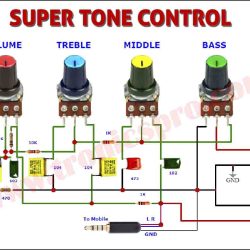
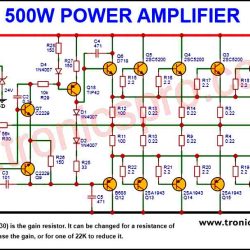
Circuit Diagram
of Bass amplifier surround sound
More Circuit Layouts





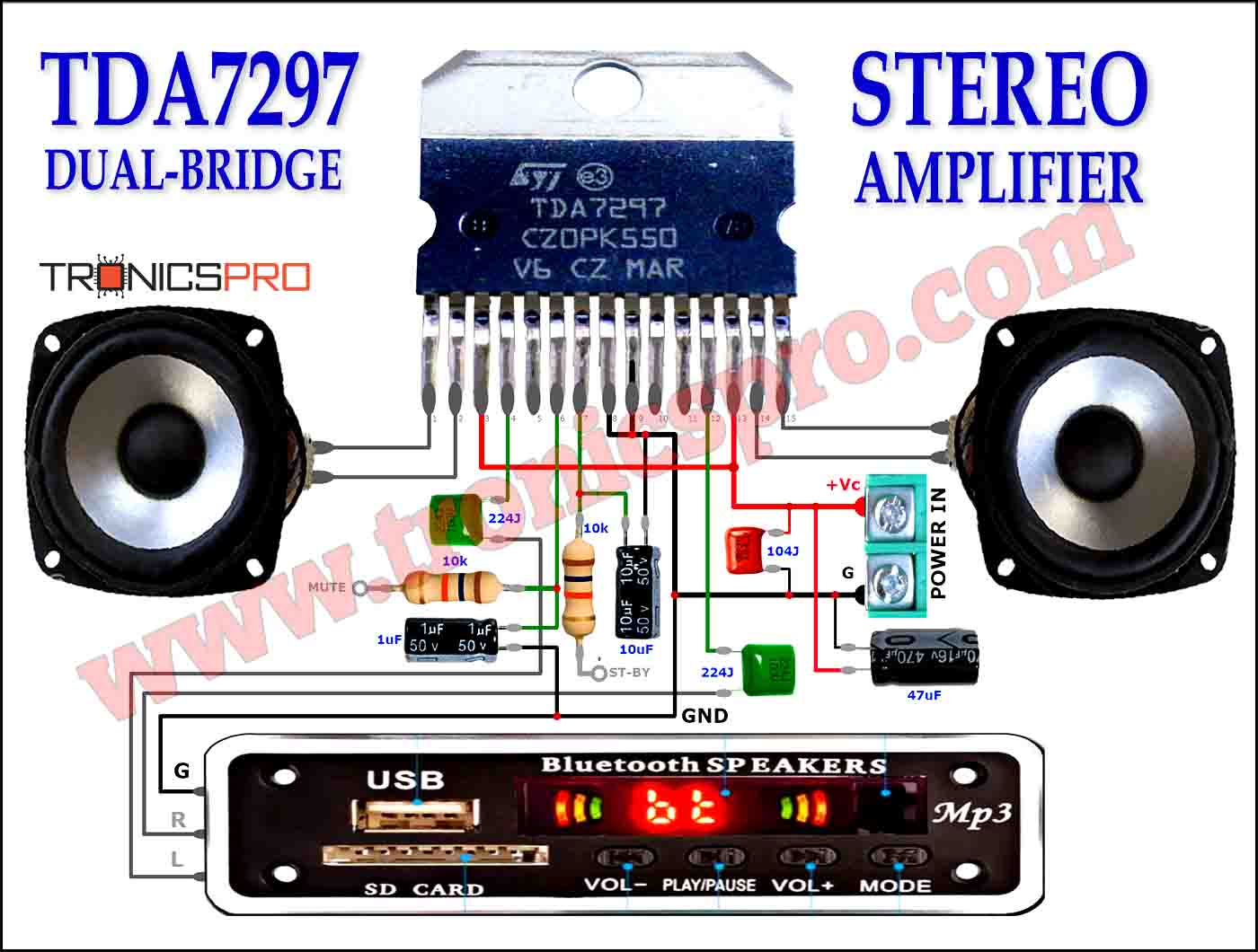

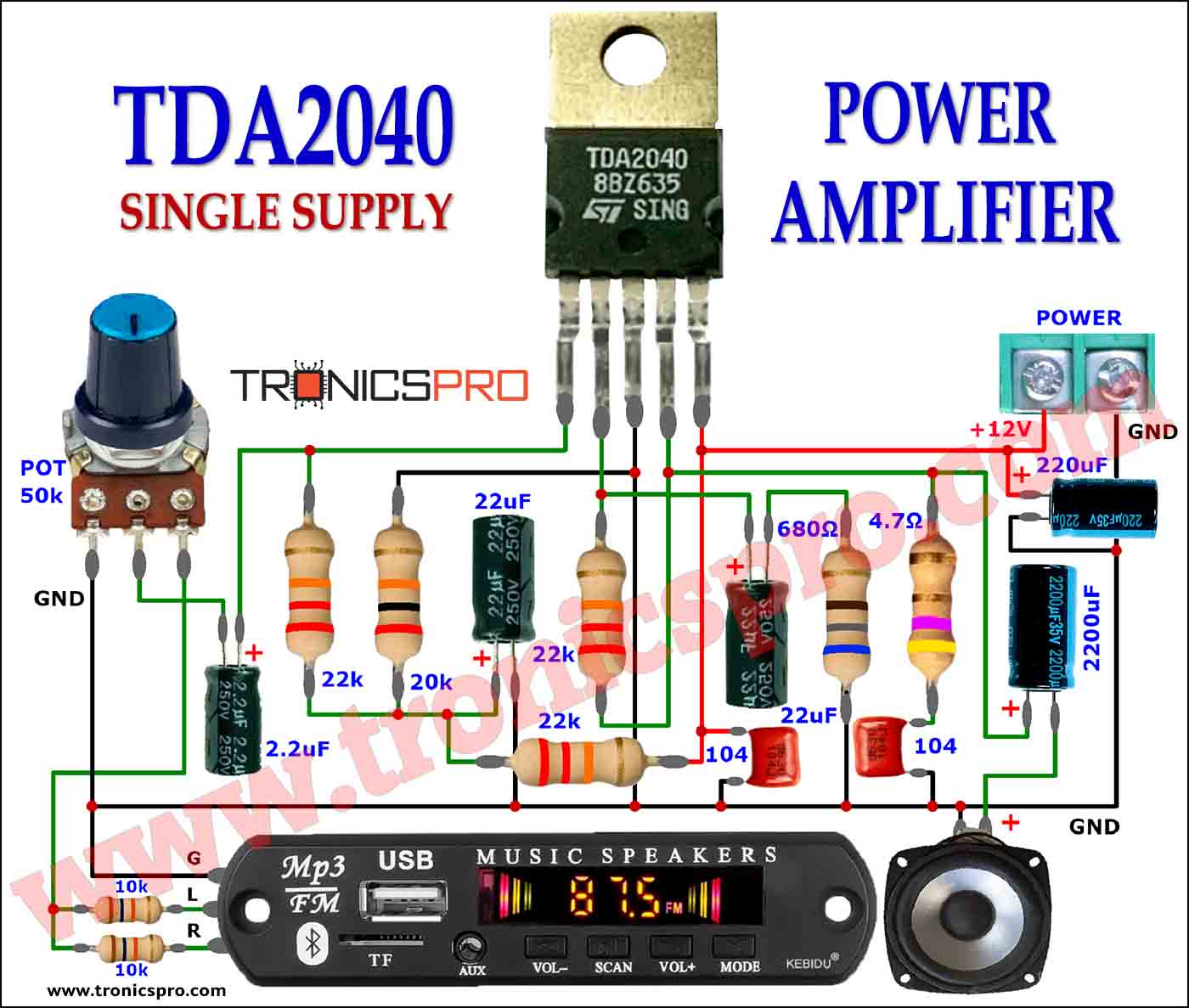
Components List
of Bass amplifier surround sound
- Resistors:
- R1‚R2 = 47 k
- R3, R4 = 4.7 k
- R5, R6 = 100 ohms
- R7 = 8.2 k
- P1 = 47 k logarithmic potentiometer
- P2 = 10 k, linear stereo potentiometer
- Capacitors:
- C1 = 22 pF
- C2 = 0.22 pF
- C3= 0.18 uF
- C4-C7 = 0.1 uF
- C8, C9 = 4.7 uF, 63 V, radial
- C10, C11 = 22 uF, 40 V, radial
- C12-C15 = 0.047 uF ceramic
- Semiconductors:
- D1‚ LED, high efficiency
- Miscellaneous:
- K1-K6, K8-K9 = audio socket for board mounting
- K7 = 2-way terminal block, pitch 7.5 mm
- B1 = B80C1500
- Tr1 = mains transformer, 2×15 V secondaries,1.5 VA
Working Explanation
of Bass amplifier surround sound
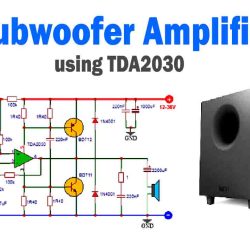
The extension is meant primarily for surround sound installations that want a few boosting of the bass frequencies however wherein a further subwoofer can not be afforded. It is primarily based totally on a disused mono AF amplifier and loudspeaker. If these provide reasonable bass performance, they can be converted into a fairly good subwoofer with the aid of an active low-pass filter-see Figure 1.
The input signals for the left-hand and right-hand channels are applied to audio sockets Kâ‚ and K2 respectively. They are output via audio sockets K3 and K4 to which the surround-sound decoder is connected. The alerts of the 2 channels are summed in IC1a, which additionally capabilities as an input amplifier. The amplification, and therefore the sensitivity of the ‘sub-woofer’, can be adjusted with P1.
The output of IC1a is carried out to a 2nd-order Butterworth low pass filter. The cut-off frequency of this energetic filter may be set between 40 Hz and 120 Hz with a dual pole potentiometer which is P2. The response characteristic of the filter at both these frequencies is shown in Figure 2. The real cut-off relies upon individual taste. The mono amplifier is connected to audio output sockets K5 and K6.
The power supply for the circuit is simple and consists of a small mains transformer, Tr1, a bridge rectifier, B1, antihunt capacitors C12-C15, a number of smoothing and decoupling capacitors, and a pair of integrated voltage regulators, which are IC2‚ and IC3.
PCB Layout (Front & Rear)


The printed circuit board is recommended, as shown above, is best built which is, however, not commercially available, but may be made with the aid of the relevant track layout.
The filter should be housed in a metal enclosure. Also, P1‚ and P2 should preferably be typed with a metal case. Hum is prevented by earthing the case and the enclosure.
The harmonic distortion is 0.0016% 30 Hz, with two input signals of 200 mV and a bandwidth of 22 kHz.
Although now no longer of top significance at low frequencies, the polarity of the subwoofer needs to be the opposite of that of the rest of the system on the grounds that the prevailing circuit inverts the signals.
Conclusion
When it comes to finding the perfect bass amplifier, it’s important to know what you’re looking for. There are a variety of different types and brands available, so take your time and do your research. Consider the size, power output, number of channels, versatility, connectivity options, and additional features that may be useful for your playing style. Ultimately, your personal preference will be the deciding factor in which amp is best for you. With so many great choices out there – from vintage classics to modern workhorses – the conclusion of bass amplifier selection can only lead to music-making bliss!