The 2N2905 pinout describes the electrical connection layout of this classic PNP silicon transistor, which is widely used in low-power switching, linear amplification, and audio signal control circuits. With excellent current handling and thermal stability, the 2N2905 remains a popular choice for designers needing reliability and consistency. This transistor provides moderate power output, good gain characteristics, and robust performance across a wide temperature range.

Introduction to 2N2905 PNP Transistor
The 2N2905 transistor is a general-purpose PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) built in a durable TO-39 metal package. It is designed for medium-current, low-voltage amplification, and switching applications. Known for its stability and linear response, the transistor is ideal for analog amplification stages, driver circuits, and audio output stages in low-to-medium-power systems.
Engineers often select the 2N2905 because of its versatility in both commercial and industrial applications. It can drive small relays, lamps, and transistors or function in complementary push-pull stages alongside its NPN counterpart, the 2N2222.
2N2905 PNP Transistor

Pinout of 2N2905

Pin Configuration of 2N2905 Pinout
| Pin# | Pin Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter |
| 2 | Base |
| 3 | Collector |
Key Features of 2N2905 Transistor
- Excellent linear amplification performance
- Stable operation over a wide temperature range
- Low leakage current characteristics
- High durability in switching circuits
- Suitable for both low and medium power stages
- Reliable operation in analog driver designs
2N2905 Transistor Datasheet and Specifications
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): –40 V
- Collector-Base Voltage (Vcb): –60 V
- Collector Current (Ic): –600 mA
- Total Power Dissipation (Ptot): 600 mW
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 100 (typical)
- Transition Frequency (fT): 200 MHz (typical)
- Junction Temperature (Tj max): 200 °C
- Package Type: TO-39 Metal Can
- Polarity: PNP
- Pin Configuration: Emitter-Base-Collector (E–B–C)
Equivalent and Alternative Transistors
Several equivalent or replacement transistors can be used in place of the 2N2905, depending on the circuit requirements:
Always verify the pin configuration and voltage ratings before substitution, as these may vary slightly among packages and manufacturers.
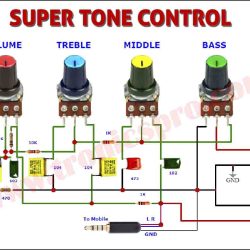
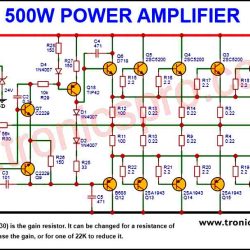
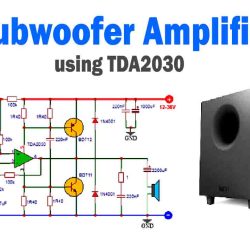
More Circuit Layouts
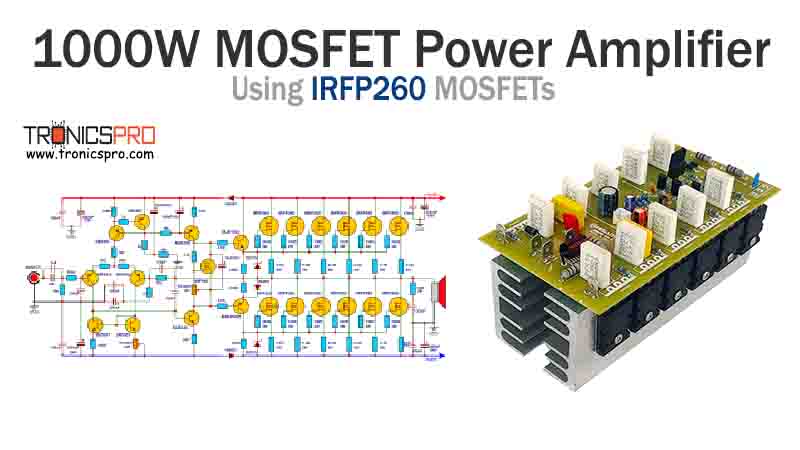
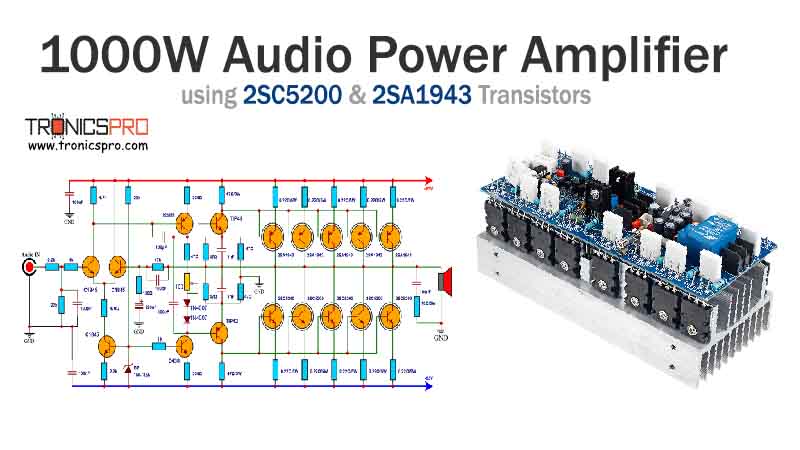
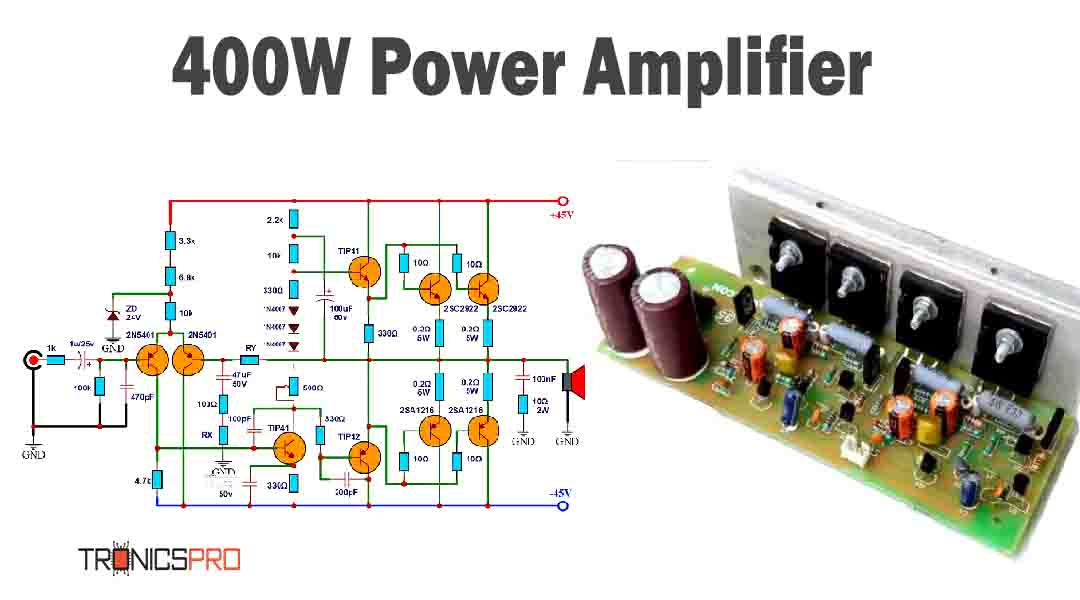
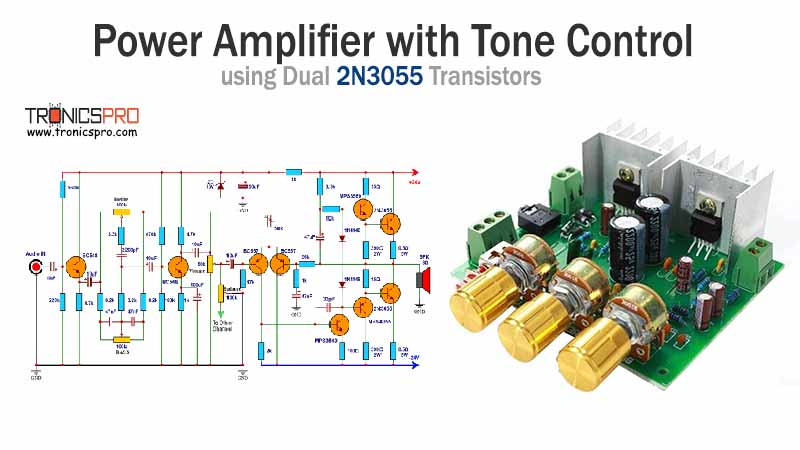

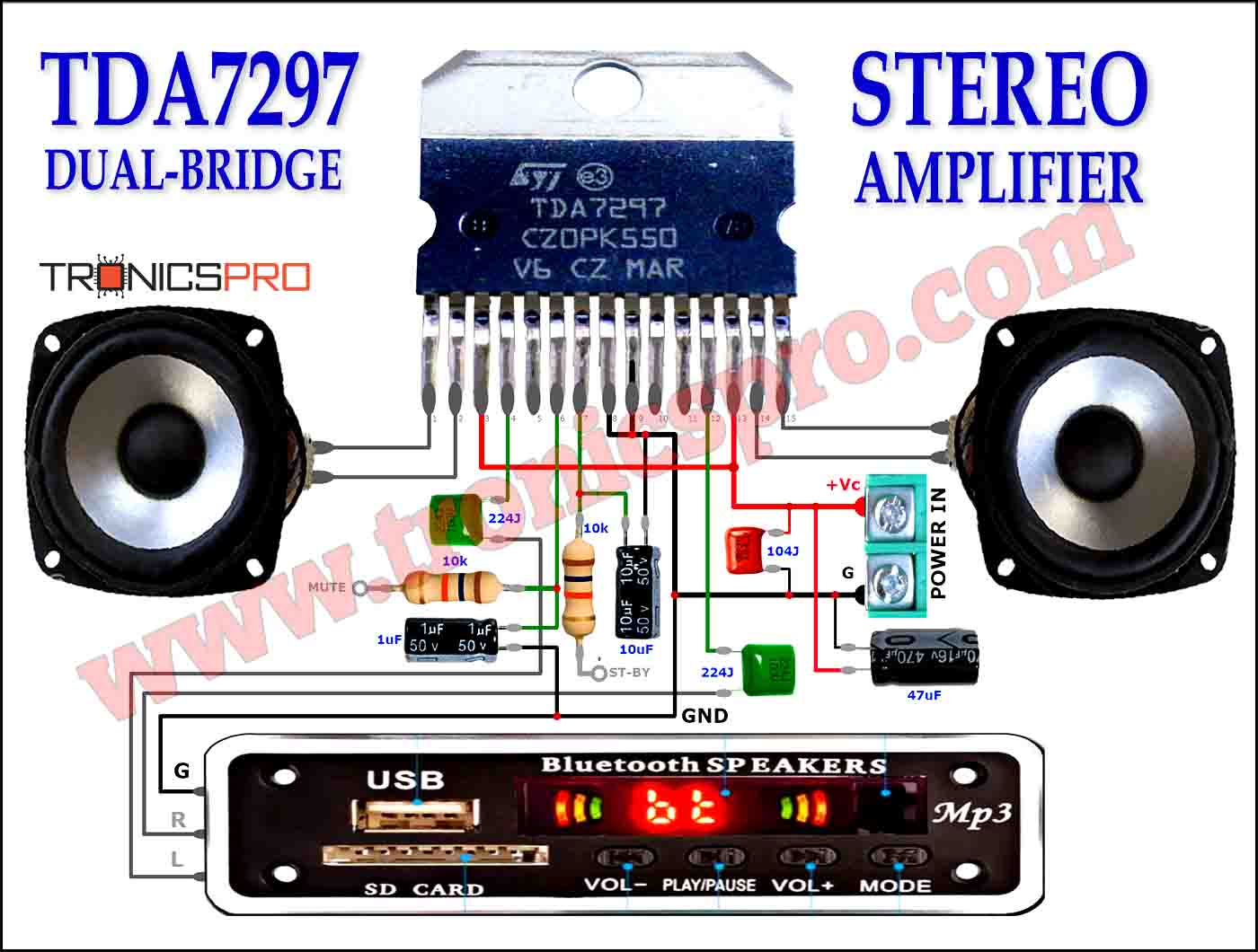

Applications of 2N2905 Transistor
- Audio amplifier stages
- Switching and driver circuits
- Signal preamplifiers
- Relay control circuits
- Voltage regulators
- Low-frequency oscillator and inverter designs
- Analog control and biasing networks
Understanding the 2N2905 Pinout Configuration
The pin configuration of the 2N2905 follows a standard Emitter–Base–Collector (E–B–C) sequence when viewed from the bottom (leads facing downward). This layout ensures easy integration with TO-39-based circuit designs and prevents wiring confusion when used in amplifier or switching circuits.
Working Principle of 2N2905 Transistor
The 2N2905 PNP transistor functions by allowing current to flow from the emitter to collector when a small base current is applied in reverse bias. When the base terminal is pulled low relative to the emitter, it enables current conduction through the collector circuit. This transistor can therefore amplify weak signals or act as a low-side switch for various loads.
Its balanced parameters make it ideal for audio preamplifiers, signal processing stages, and driver amplifiers, providing clean signal reproduction and stable performance even under varying operating conditions.
Comparison Summary — 2N2905 vs 2N2907
The 2N2907 is a close electrical match to the 2N2905, both being PNP silicon BJTs with similar gain and current capabilities. However, the 2N2907 is typically packaged in TO-18, offering smaller physical dimensions, while the 2N2905 uses a TO-39 metal case that allows slightly higher thermal dissipation.
In practical circuits, both devices perform similarly in switching and amplification roles. The 2N2905 provides better mechanical strength and higher power handling due to its metallic encapsulation, making it more suitable for medium-power audio and driver stages.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the 2N2905 transistor used for?
It is commonly used in audio amplifiers, signal drivers, and relay switching applications where moderate current and voltage control are needed.
What type of transistor is 2N2905?
The 2N2905 is a PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) used for general-purpose amplification and low-frequency switching.
What is the 2N2905 pin configuration?
It has an Emitter-Base-Collector (E–B–C) pin sequence when viewed from the bottom of the TO-39 package.
Is 2N2905 the same as 2N2905A?
The 2N2905A is a variant with higher voltage tolerance, but both have nearly identical electrical characteristics and pinouts.
Can I replace 2N2905 with 2N2907?
Yes, the 2N2907 can serve as a substitute in many circuits if power dissipation and package constraints are acceptable.
Conclusion
The 2N2905 transistor remains a durable and high-quality component for engineers building analog or switching circuits. Its moderate current capacity, reliable gain, and excellent thermal stability make it suitable for a broad range of medium-power designs. When selecting a PNP transistor, the 2N2905 offers a trusted balance of performance and availability, especially in classic amplifier and driver configurations.
Datasheet & Pinout of 2N2905 PNP Transistor
Click the following Button to download the datasheet of 2N2905 Transistor :
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.