Introduction
In today’s technologically advanced world, batteries play a pivotal role in powering a wide range of devices, be it remote controls, smartphones, or even electric vehicles. However, constantly purchasing and replacing batteries can be expensive and environmentally unfriendly. That’s where having an automatic battery charger comes in handy. In this article, we will explore how to make a 1.2V automatic battery charger using LM393 IC, LF33CV IC, BC557 transistor, and a 5K trimpot. With this simple yet effective circuit, you can effortlessly charge your batteries, ensuring they are always ready to power your devices. Also we will describe all the major components mentioned above, one by one separately for your better understanding the project.
Introduction to Major Components:
LM393 IC
The LM393 is a widely used integrated circuit that consists of two independent voltage comparators. It operates with a single power supply and can detect variations in voltage levels with high precision. The LM393 IC is commonly used in battery chargers due to its efficiency and accuracy in monitoring the charging process.
LF33CV IC
The LF33CV IC is a low dropout voltage regulator that regulates the output voltage with excellent precision. It is specifically designed for use in battery charging applications where a constant voltage output is required. The LF33CV IC has a low dropout voltage, which means it can regulate the output voltage even when the input voltage is slightly lower than the required voltage level.
BC557 Transistor
The BC557 transistor is a commonly used PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT). It is ideal for amplification and switching applications, making it a suitable choice for our automatic battery charger circuit. The BC557 transistor facilitates the charging process by controlling the current flow to the battery based on the voltage levels detected by the LM393 IC.
5K TRIMPOT
The 5K trimpot, also known as a trimmer potentiometer, is an adjustable resistor that allows us to precisely set the desired voltage level. In our 1.2V automatic battery charger circuit, the 5K trimpot is used to adjust the charging voltage to the recommended 1.2V for efficient and safe battery charging.

Circuit Diagram of 1.2V Automatic Battery Charger
This project can be designed using a few basic components. The circuit diagram of this project is shown below.
More Circuit Layouts

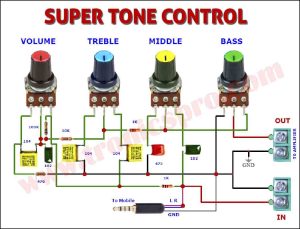




Components List of 1.2V Automatic Battery Charger
Following is the list of all components used in this project:
- 1x LM393 IC
- 1x LF33CV IC
- 1x BC557 TRANSISTOR
- 4x 1N4148 DIODES
- 2x LEDS
- 2x 10uF CAPACITORS
- 1x 5K TRIMPOT
- 1X 1 OHM RESISTOR
- 2X 100 OHM RESISTORS
- 1X 470 OHM RESISTOR
- 1X 10K RESISTOR
- 1x 2 PIN TERMINAL BLOCK
- PREF BOARD
- JUMPER WIRES
Explanation of 1.2V Automatic Battery Charger
Circuit Description
Now that we understand the significance of these components, let’s move on to the construction of the 1.2V automatic battery charger circuit. Firstly, gather all the necessary components mentioned above in Components List section. You can easily acquire them from local electronic stores or online platforms. Once you have everything, it’s time to start assembling the circuit.
To build the 1.2V automatic battery charger, we need to connect them in a specific circuit configuration. The circuit diagram of the project is provided above for ready reference. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Place LM393 IC on the board and connect its pin-4 to ground, pin-8 to positive supply. Now connect 1n4148 diode cathode to pin-2 and anode to ground. Connect 10k resister to pin-2 to positive supply which will come from pin-3 of LF33CV IC.
- Now place a 5k timpot and connect its center pin to pin-3 of LM393 IC. Now connect its pin-2 to ground while pin-1 will be connected to the positive side of battery compartment.
- Now place a BC557 transistor and connect its pin-3 to positive supply. Take a 470 ohms resister and connect its one side to pin- of BC557 transistor and the other side to pin-1 of LM393 IC.
- Place a 2 pins terminal block and connect to with the positive and negative of the power supply.
- Place one LF33CV regulated IC and connect its pin-3 to pin-3 of BC557 transistor, its pin-2 to ground and pin-1 to the positive of terminal block.
- Take two 10 uf capacitors and connect one of them positive pin to positive of terminal block and second capacitors positive to pin-3 of LF33CV IC. While negative of of both capacitors will be connected to the ground.
- Connect a 100 ohms resister to pin-1 of BC557 transistor and the other side to the anode of LED while the cathode of LED will be ground.
- Connect one 1n4148 diode’s anode to pin-1 of BC557 transistor and cathode to the cathode of a Green LED while the anode of Green LED will be connected with pin-3 of BC557 transistor. Also connect a 100 ohms resister to the cathode of Green LED and its other side will be grounded.
- Take two more 1n4148 diodes and connect anode of one diode to pin-1 of BC557 transistor while its cathode to the anode of the other diode. The cathode of the other diode will be connected with a 1 ohm resister while the other side of 1 ohm resister will be connected with the positive of the battery compartment. Also connect the negative side of the battery compartment to ground.
Working Principle of 1.2V Automatic Battery Charger
Now that we have successfully constructed the circuit, it’s essential to understand how it operates. The LM393 IC constantly compares the voltage level of the battery with the reference voltage obtained from the 5K trimpot. When the battery voltage falls below the reference voltage, the LM393 IC sends a signal to the BC557 transistor, turning it on and allowing current to flow from the power source to the battery via the LF33CV IC. As a result, the battery starts to charge. Once the battery voltage reaches the reference voltage, the LM393 IC switches off the BC557 transistor, effectively stopping the charging process. This automatic mechanism prevents overcharging and extends the battery’s overall lifespan.
Conclusion of 1.2V Automatic Battery Charger
In conclusion, constructing a 1.2V automatic battery charger using the LM393 IC, LF33CV IC, BC557 transistor, and 5K trimpot provides a cost-effective and eco-friendly solution to keep your batteries charged. By utilizing the voltage comparator, voltage regulator, and switch functionality of these components, this circuit ensures efficient and safe charging for your batteries. With this knowledge, you can now embark on building your own battery charger, empowering you to save money and contribute towards a sustainable future.
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- 12V-220V H-Bridge Inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- 18650 battery bank free charge protection module
- D718 B688 Bass Amplifier Homemade DIY
- C5200 Bass Amplifier DIY Homemade with Volume
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
- C5200 A1943 TDA2030 Amplifier DIY Homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!
Thanks for visiting the article and watching the video.

























seems good