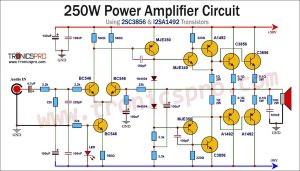
following is the 100 Watts LM3886 Amplifier Circuit Diagram. The LM3886 from National Semiconductor is a high-performance 150 W audio power amplifier with a mute. Its performance, using the self-peak instantaneous temperature (K) (SPIKe) protection circuitry, is better than discrete and hybrid amplifiers since it provides an inherently, dynamically protected safe operating area. The LM3886T belongs to the TO220 package and comes in lead non-isolated, 11 staggered.
For take-a-look purposes, the prototype of the amplifier became powered via way of means of a stabilized ±35 V supply. The most electricity of approximately 63 watts into eight ohms undistorted output became acquired at a drive level of 1 Vrms. Lowering the load impedance to 4 ohms raises the output power to 108 watts. Just keep in mind that the amplifier will not be powered by a regulated Power supply.
Circuit Diagram
of 100 Watts LM3886 Amplifier
More Circuit Layouts





LM3886T Pinout

Working Explanation
of 100 Watts LM3886 Amplifier
Pay attention to heat dissipation of the amplifier IC. A strong and large enough heat sink is offered as specified in the parts list is sufficient for load impedances of 6 ohms or more. Even if a heat sink with a thermal resistance lower than 1 KW-1 is employed, the amplifier IC will cause a ‘hot spot’ on the heat sink surface where the actual thermal resistance is plenty better regionally than the specification. With this in thoughts, it’s far advocated to drop the delivery voltage to about ±30 V if the amplifier is used to pressure a four-ohm load. Also, endure in thoughts that heatsink separating substances like mica or even ceramics generally tend to elevate the thermal resistance via way of means of 0.2 KW-1 to 0.4 KW-1. The steel tab in the back of the IC is at a negative supply potential.
The C6-R6 are not essentially required in this project and could be omitted unless the output of the amplifier is found to be unstable as a result of an application that is very much different as shown here.
Populating the amplifier board is straightforward, and most of the time required to build the amplifier will be spent in drilling, cutting, mounting, and isolating the heat sink. Since the electrolytic capacitors are rated at 40 volts, the supply voltage must not exceed that level. The PCB may be made with the aid of the track layout.
Components List
of 100 Watts LM3886 Amplifier
- Brief parameters:
- Input sensitivity: 1 Vrms (63 W into 8 W)
- Output power, 8 Q: 63 W (THD <1%) Output power, 4 Q: 108 W (THD <1%)
- Damping factor (8 Q) >450 at 1 kHz>170 at 20 kHz
- Slew rate: >10 V/ms (rise time = 5 ms)
- Power bandwidth: 8 Hz to 90 kHz
- Signal/noise ratio: 94 dBA (1 W into 8 W)
- Quiescent current: 50 mA
- Input sensitivity: 1 Vrms (63 W into 8 W)
- Output power, 8 Q: 63 W (THD <1%) Output power, 4 Q: 108 W (THD <1%)
- Damping factor (8 Q) >450 at 1 kHz>170 at 20 kHz
- Slew rate: >10 V/ms (rise time = 5 ms)
- Power bandwidth: 8 Hz to 90 kHz
- Signal/noise ratio: 94 dBA (1 W into 8 W)
- Quiescent current: 50 mA
Resistors: - R1, R3 = 1 kQ
- R2, R4, R5, R8, R9 = 102 kQ
- R6 = not fitted, see text
- R7 = 10 Q, 5 W
Capacitors: - C1 = 2.2 uF, metalized polyester (MKT), pitch 5 mm or 7.5 mm
- C2 = 220 pF, 160 V, axial, polystyrene
- C3 = 22 uF, 40 V, radial
- C4 = 47 pF, 160 V, axial, polystyrene
- C5 = 100 uF, 40 V, radial
- C6 = not fitted, see text
- C7, C8 = 0.1 uF
- C9, C10 = 2200 uF, 40 V, radial, max. diameter 16 mm
Inductors: - L1 = 0.7 mH, 13 turns of 1.2-mm diameter (18
SWG) enameled copper wire, 10 mm internal
diameter wound around R7.
Integrated circuits: - IC1 = LM3886T (National Semiconductor)