The BD378 pinout refers to the leg arrangement of the BD378 PNP power transistor, which is commonly used in audio amplifier circuits, linear regulators, and medium-power switching applications. This transistor provides strong performance in the TO-126 package, with a collector-emitter voltage of −60V, a collector-base voltage of −75V, and a power dissipation capacity of up to 25W. It’s the PNP complementary transistor to the BD377 NPN, making them ideal for push-pull or Class AB amplifier configurations.
Introduction to BD378 PNP Transistor
The BD378 PNP transistor is a silicon-based device designed for medium power amplification and switching operations. It is widely used in audio amplifier output stages, motor drivers, and signal amplifiers, where its balance of current gain, voltage tolerance, and thermal stability ensures reliable performance.
This transistor features a maximum collector current of −4A, enabling it to handle significant load currents in both analog and digital circuits. The TO-126 package provides excellent heat dissipation, allowing it to operate under moderate power without requiring an excessive heatsink.
Being the PNP counterpart of BD377, the BD378 transistor complements its NPN partner in push-pull amplifier circuits, offering symmetrical drive capability and stable thermal characteristics.
BD378 PNP Transistor

Pinout of BD378
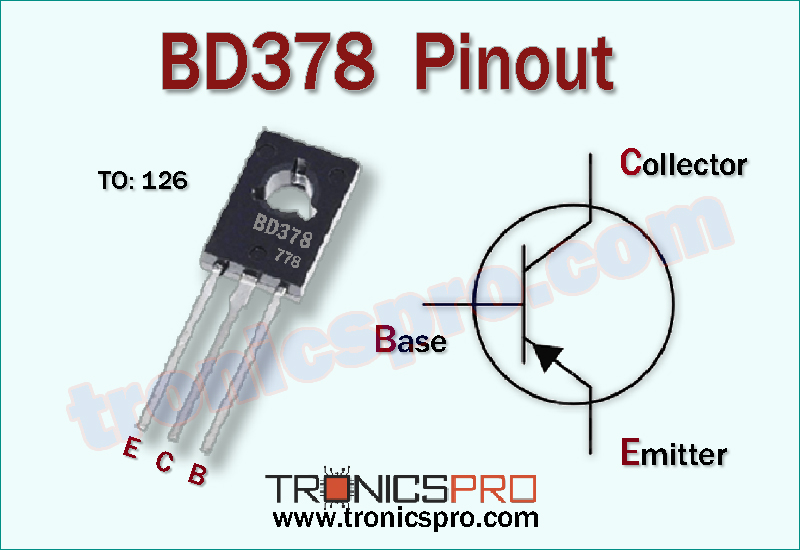
Understanding the BD378 Pinout Configuration
The BD378 pinout is straightforward and follows the standard TO-126 transistor package layout. When viewing the flat side of the transistor with leads downward, the pins are arranged as follows:
Pin Configuration of BD378 Pinout
| Pin# | Pin Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter |
| 2 | Collector |
| 3 | Base |
This configuration is identical to many other BD-series power transistors, simplifying circuit design and replacement.
Key Features of BD378 Transistor
- Designed for medium-power amplification and switching
- PNP silicon transistor with complementary NPN pair (BD377)
- Provides high reliability and stable thermal operation
- Suitable for linear and Class AB amplifier stages
- Compatible with TO-126 standard transistor footprint
- Offers good current gain with low saturation voltage
- Ideal for push-pull configurations in audio circuits
- Works efficiently in both analog and switching applications
- Supports symmetrical circuit design for balanced performance
- Rugged and durable for industrial and hobby-grade projects
BD378 Transistor Datasheet and Specifications
The BD378 transistor datasheet highlights its use in medium-voltage, medium-power linear and switching circuits. Below are the main specifications derived from verified datasheet information:
- Transistor Type: PNP Silicon
- Package: TO-126
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vce): −60V
- Collector-Base Voltage (Vcb): −75V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (Veb): −5V
- Collector Current (Ic): −4A
- Power Dissipation (Pc): 25W
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 to 160
- Transition Frequency (fT): 3 MHz
- Operating Temperature: −55°C to +150°C
These characteristics make BD378 a strong performer in amplifier output drivers, voltage regulators, and power control circuits.
Working Principle of BD378 Transistor
As a PNP transistor, the BD378 operates when a small negative voltage is applied to the base relative to the emitter. Current flows from the emitter to collector when the base-emitter junction is forward biased.
In amplifier circuits, the BD378 allows current to flow proportionally to the input signal applied at the base, producing a magnified output at the collector terminal. In switching circuits, it acts as a low-loss electronic switch, turning “ON” when the base is sufficiently negative with respect to the emitter and “OFF” when this voltage is removed.
Because of its balanced voltage and current ratings, the BD378 works efficiently in both analog linear applications and digital switching operations.
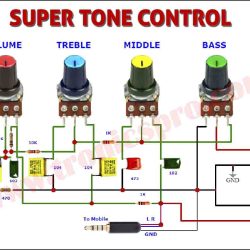
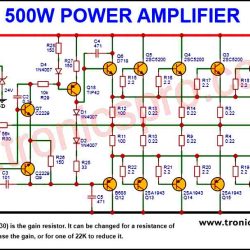
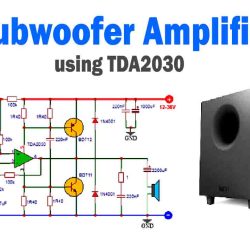
More Circuit Layouts
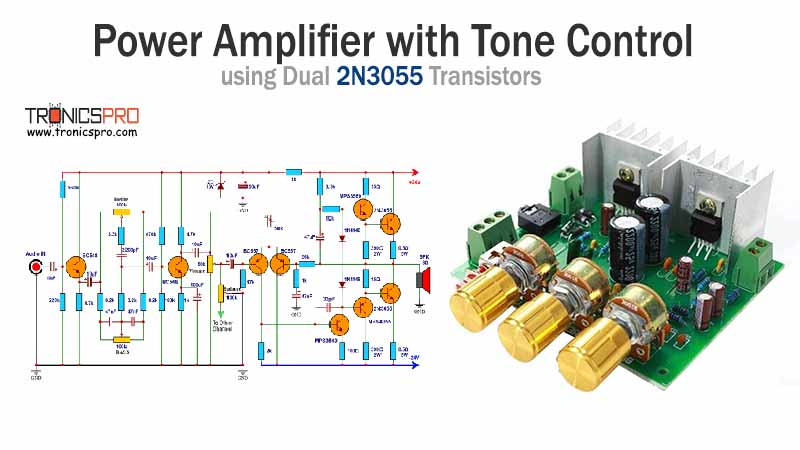

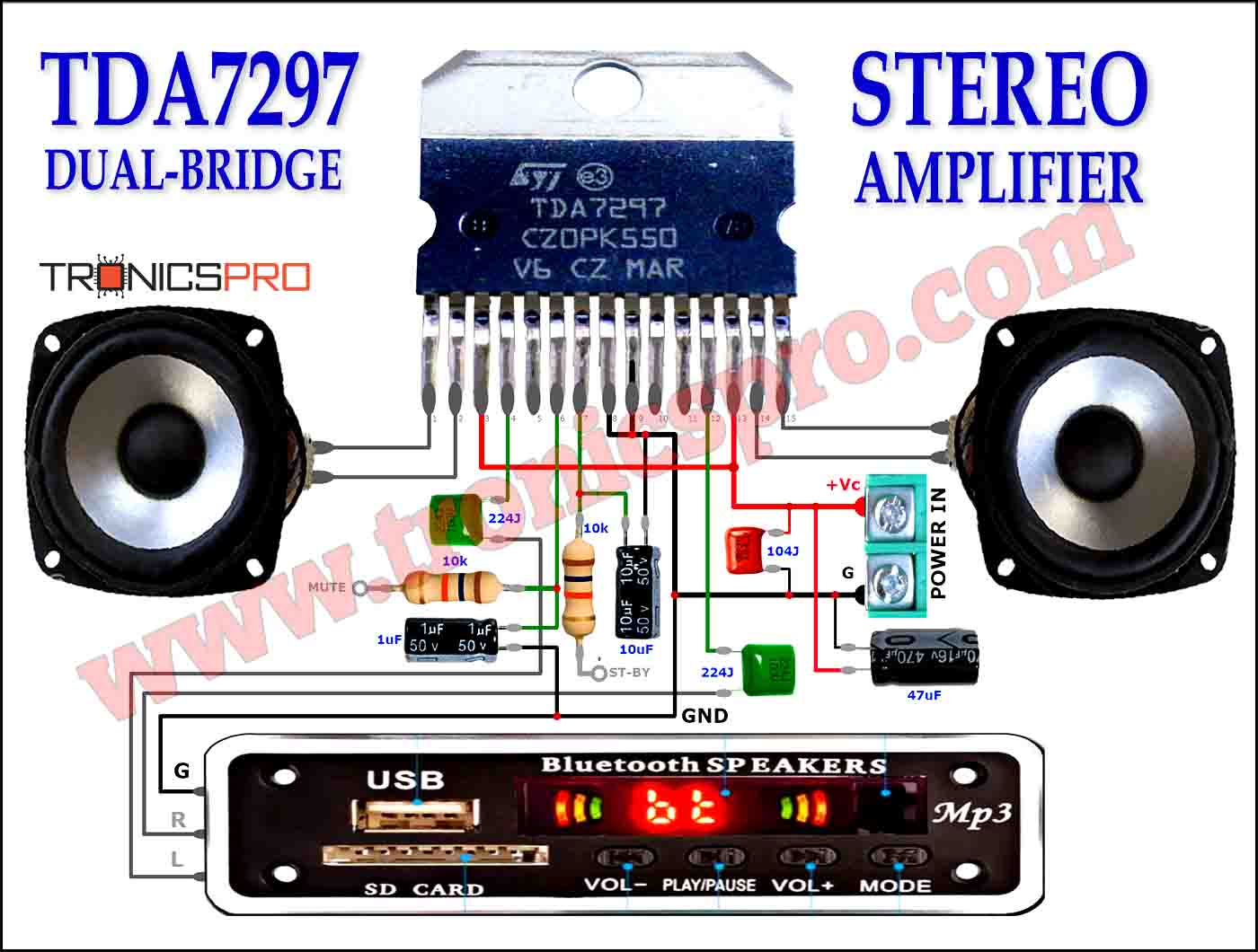

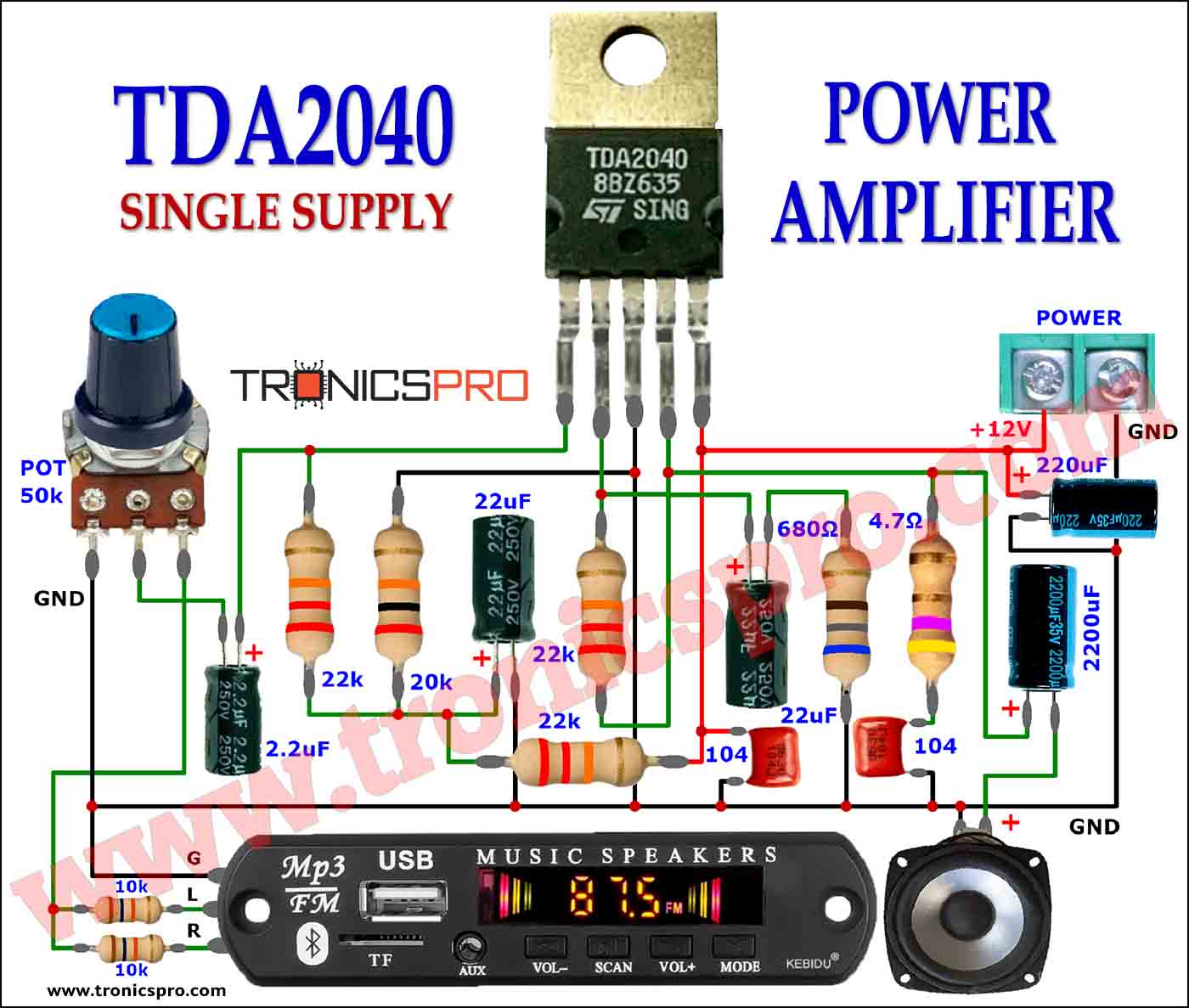
Typical Applications of BD378
- Audio Power Amplifiers (Push-Pull Stages)
- DC Motor Drivers
- Power Supply Regulation Circuits
- Relay and Lamp Drivers
- Voltage Regulators and Power Control Circuits
- Inverter and Converter Output Stages
- Complementary Pair Amplifiers with BD377
The BD378 transistor is particularly favored in stereo amplifier designs and audio output drivers, where it ensures distortion-free and thermally stable performance when paired with BD377.
NPN Complementary Transistor
The NPN complementary transistor of BD378 is the BD377, and vice versa. These two devices are designed to work together in circuits requiring complementary symmetry.
The BD377 handles the positive signal swing (NPN), while BD378 manages the negative swing (PNP), making them perfect for Class AB amplifier outputs and balanced driver circuits.
Equivalent Transistors and Alternatives
If BD378 is unavailable, you can use one of the following equivalent or alternative transistors, provided you verify pin configuration and ratings:
- BD646 (similar power range, PNP)
- BD436 (lower power, PNP)
- 2N2955 (metal case PNP, higher power)
- TIP32C (slightly higher voltage tolerance)
- MJE2955 (similar performance in TO-220 package)
When replacing, ensure that the Vce, Ic, and hFE ratings match your application requirements for safe operation.
BD378 vs BD377 Comparison
The BD378 (PNP) and BD377 (NPN) transistors are complementary counterparts designed for high-efficiency, medium-power applications. Both share identical maximum ratings of 60V (Vce) and 25W of power dissipation, with the only distinction being their polarity and conduction type.
While BD377 conducts current when its base is driven positive, BD378 conducts when its base is driven negative. This makes them ideal for pairing in push-pull audio amplifier configurations, where one handles the positive half-cycle and the other the negative.
In practical terms:
- BD377 is used in the high-side (NPN) stage of the amplifier.
- BD378 is used in the low-side (PNP) stage.
Together, they deliver balanced amplification, improved linearity, and efficient power handling. If a circuit uses BD377 for the positive output stage, BD378 is the correct complementary component for the negative phase.
In short, BD377 and BD378 are like mirror images in function — both providing the same performance levels but opposite current flow direction, ensuring symmetry in high-fidelity amplifier systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the BD378 transistor used for?
The BD378 transistor is mainly used for audio power amplification, driver circuits, and power regulation. It is commonly paired with BD377 for complementary Class AB designs.
Is BD378 a PNP or NPN transistor?
The BD378 is a PNP transistor.
What is the BD378 pin configuration?
The BD378 pinout (from left to right, flat side facing you) is: Pin 1 – Emitter, Pin 2 – Collector, Pin 3 – Base.
What is the complementary transistor for BD378?
The complementary transistor for BD378 is BD377 (NPN).
Can I use BD378 instead of BD646?
Yes, in some cases you can, provided the voltage and current requirements match. BD378 typically handles similar or slightly lower voltages than BD646 but performs well in medium power ranges.
Conclusion
The BD378 transistor is a robust and reliable PNP power transistor, ideal for audio amplifiers, motor drivers, and medium-load switching circuits. With a collector-emitter voltage of −60V, power dissipation of 25W, and complementary pairing with BD377, it offers an excellent balance of efficiency, performance, and compatibility.
Its TO-126 package, standard pinout, and strong electrical characteristics make it a long-standing favorite among hobbyists, technicians, and circuit designers who need dependable results in medium-power electronic systems.
Datasheet & Pinout of BD378 NPN Transistor
Click the following Button to download the datasheet of BD378 Transistor :
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article