Introduction
The BD140 is a popular PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) known for its robustness and versatility in medium-power electronic circuits. As a key member of the BD series, it is a go-to component for a wide range of applications, from educational projects to commercial electronics. Its ability to handle a significant collector current of up to -1.5A allows it to drive demanding loads such as high-power LEDs, relays, and motors, making it an effective electronic switch.

NOTE: If you want to download the DATASHEET, the download button is provided end of this article.
The transistor’s high voltage ratings make it a reliable choice for various circuit designs. With a collector-emitter and collector-base voltage of -80V, the BD140 can safely operate in circuits running at or below 80V DC. This durability, combined with its substantial collector dissipation of 12.5 watts, makes it an excellent transistor for audio amplifier circuits, where it can manage the heat generated during signal amplification. The low saturation voltage of -0.5V ensures minimal voltage drop and power loss when the transistor is in its “on” state.
BD140 PNP Transistor

The BD140 is most famous for being the complementary partner to the NPN transistor BD139. This pair is fundamental to the design of efficient Class B push-pull amplifiers, where the BD140 handles the negative half of the audio signal while the BD139 handles the positive half. This powerful combination allows for high-fidelity audio output with minimal distortion. This balance of features—high current handling, robust voltage ratings, and excellent power dissipation—secures the BD140’s place as an indispensable component for both switching and amplification purposes.
BD140 Pinout

BD140 PNP Transistor Key Features
The BD140 is a popular PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for medium-power applications. It is a key component in the BD series and serves as the complementary opposite to the BD139 NPN transistor.
- PNP Transistor: The BD140 is a PNP device, which means that its operation is controlled by a negative voltage at its base. A current flows from the emitter to the collector when the base is biased with a negative voltage. This characteristic makes it suitable for use in complementary circuits with NPN transistors.
- High Current Handling: The BD140 has a maximum continuous collector current (IC) of -1.5A. This significant current rating allows it to control a variety of medium-power loads, such as motors, relays, and high-power LEDs. The negative sign indicates the direction of current flow, which is out of the collector.
- High Voltage Ratings: It features a collector-emitter voltage (VCE) and a collector-base voltage (VCB) of -80V. These high ratings make it a durable component that can be used safely in circuits operating under 80V.
- Medium Power Dissipation: The BD140 can dissipate up to 12.5 watts of power. This capability is crucial for medium-power applications like audio amplifiers, as it allows the transistor to handle and dissipate heat effectively, preventing thermal damage.
- High DC Current Gain (hFE): The transistor’s DC current gain ranges from 40 to 160, enabling it to amplify small input signals and drive larger currents. This is a key feature for its use in audio and signal amplification circuits.
- Complementary Pair: The BD140 is designed as the complementary partner to the BD139 NPN transistor. This pairing is fundamental to the design of Class B push-pull amplifiers, where they work together to efficiently amplify both the positive and negative halves of an audio signal.
- Compact Package: The BD140 is typically available in a TO-126 or SOT-32 package, which is a common through-hole format that facilitates mounting and heat dissipation.
BD140 Transistor Specifications/Characteristics
| Characterstics | Rating (Max) |
|---|---|
| Collector Current(IC): | -1.5A |
| Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): | –80V |
| Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): | –80V |
| Emitter-Base Voltage (VEBO): | –5V |
| Collector Dissipation (Pc): | 12.5 Watt |
| Transition Frequency (fT): | 190 MHz |
| DC Current Gain (hFE): | 25 – 250 |
| Storage & Operating temperature Should Be: | -55 to +150 Centigrade |
| Package Type: | TO-126 |
| Transistor Type: | PNP |
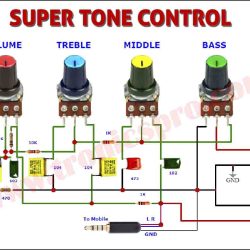
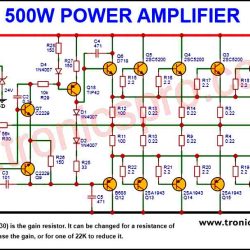
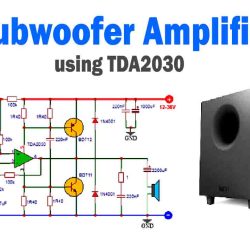
More Circuit Layouts
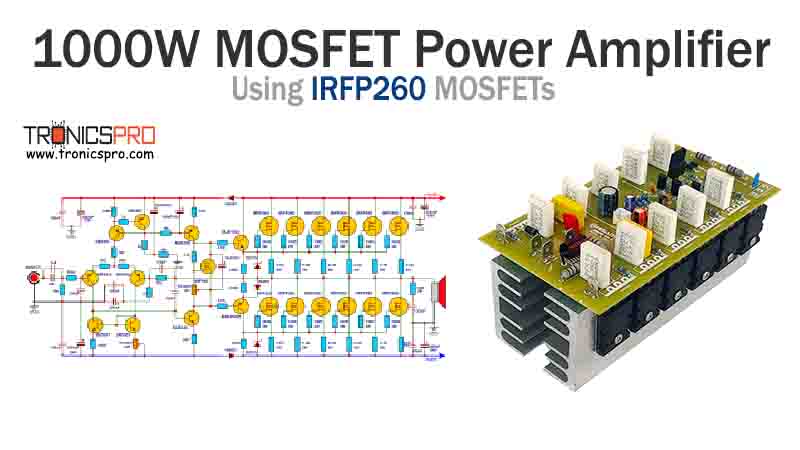
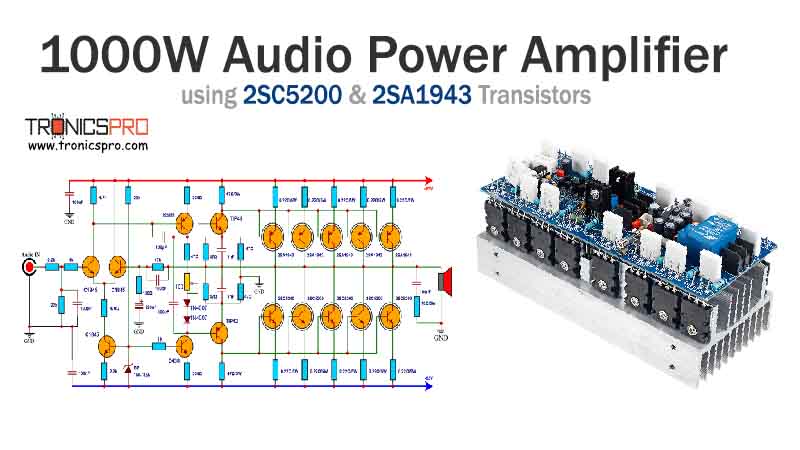
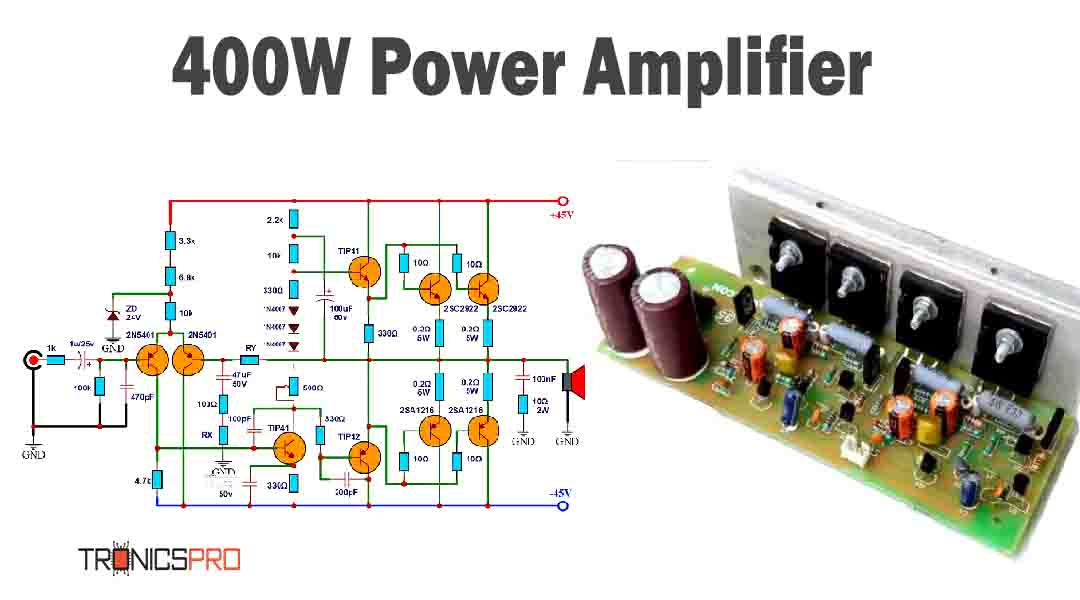
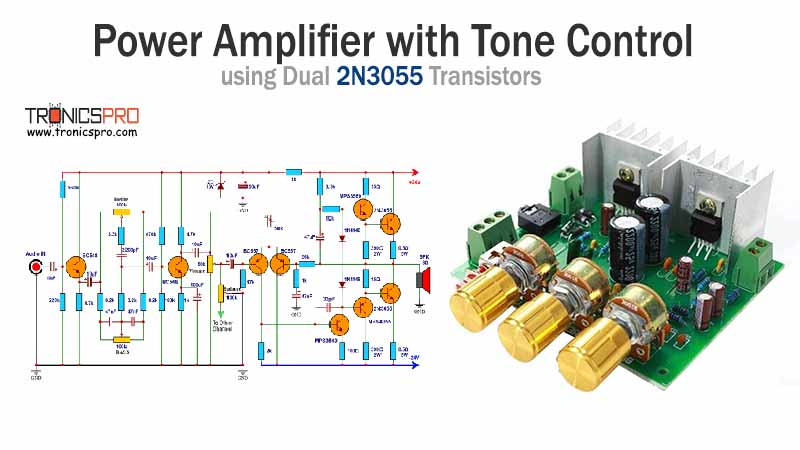

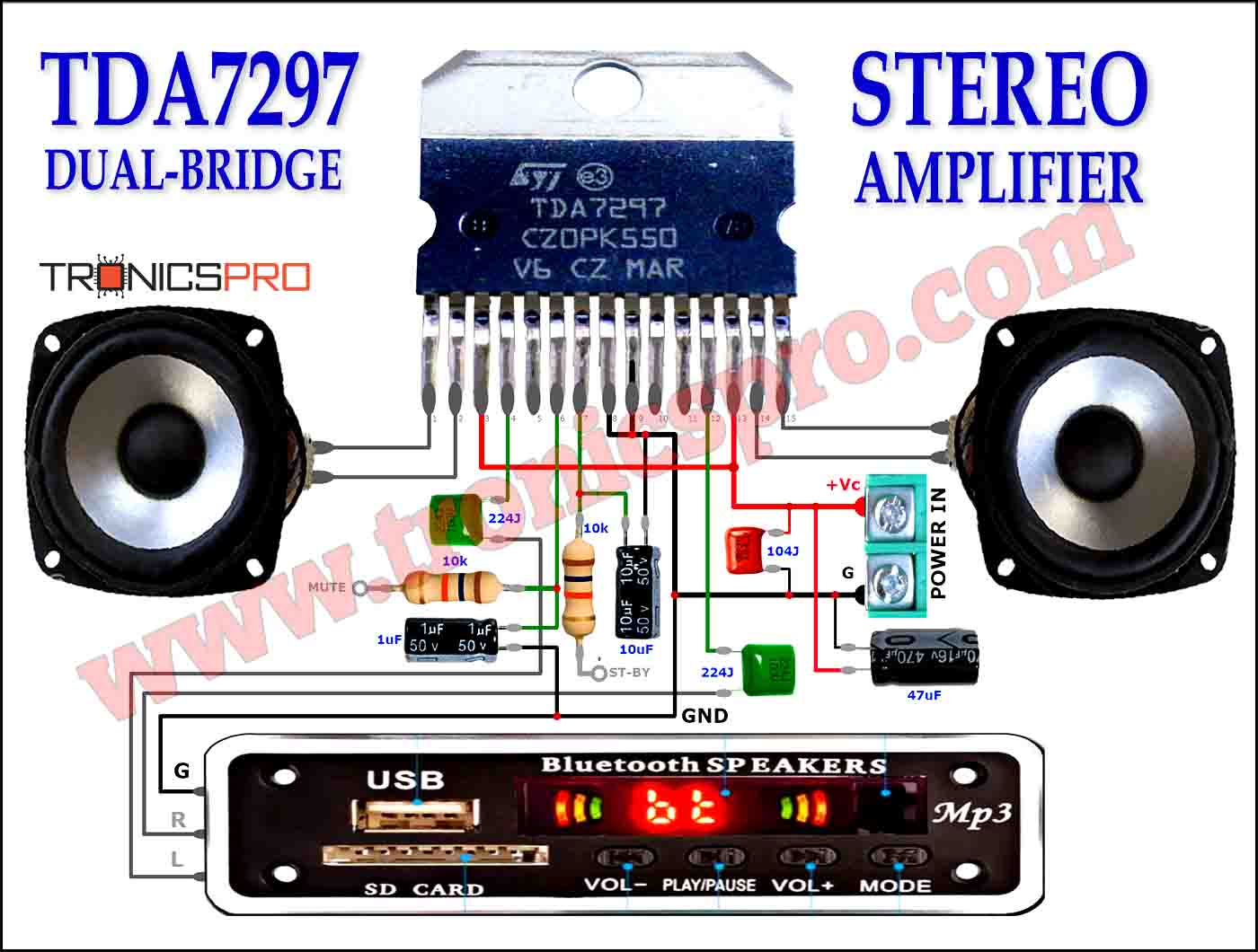

Key Applications of BD140 PNP Transistor
The BD140 is a popular medium-power PNP transistor used for both amplification and switching applications. As the complementary partner to the BD139, it’s a key component in a variety of electronic circuits.
- Audio Amplifiers: The BD140 is widely used in the driver and output stages of audio amplifiers. It’s commonly paired with the BD139 in Class B push-pull configurations, which are highly efficient and provide a powerful, low-distortion output signal for speakers.
- Switching Loads under 1.5A: With a continuous collector current of up to -1.5A, the BD140 can act as an effective electronic switch. It’s suitable for controlling medium-power loads such as relays, solenoids, and high-power LEDs in various control and automation circuits.
- Battery Chargers: The BD140 is often found in the regulation or switching stages of battery charger circuits, where it helps to manage the current flow to the battery, ensuring a safe and controlled charging process.
- Power Supplies: It can be used in power supply circuits, particularly in linear voltage regulators, to maintain a stable output voltage by acting as a pass transistor that dissipates excess power.
- Motor Driver: The BD140 is capable of driving small to medium-sized DC motors, making it a common component in motor driver circuits for robotics and other electromechanical projects.
- Darlington Pair: When combined with another transistor in a Darlington pair configuration, the BD140 can achieve a very high current gain. This is useful for applications where a small input signal needs to control a much larger load current.
- Voltage Regulation: The BD140 can be used in voltage regulator circuits to maintain a constant output voltage, making it useful in providing a stable power source for sensitive electronics.
NPN Complimentary Transistor
NPN Complementary of BD140 Transistor is BD139.
Equivalent Transistors of BD140
BD238G, MJE171, MJE702, BD792
(The pinout for certain transistors can vary from that of the BD140).
Datasheet of BD140 PNP Transistor
Click the following Button below to download the datasheet of BD140 Transistor :
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.