The KSP44 NPN transistor is a high-voltage, low-current semiconductor device commonly used in switching and signal control circuits. This article explains its electrical characteristics, typical applications, operating behavior, and detailed ksp44 pinout information to support correct and safe use in electronic designs.

Introduction
The KSP44 is an NPN bipolar junction transistor designed for high-voltage applications where moderate current handling and stable performance are required. It is widely used in display driver circuits, power control stages, and signal processing sections. The TO-92 package provides a compact form factor suitable for space-constrained PCB layouts.
Its predictable behavior and reliable construction make the KSP44 a practical choice for both industrial electronics and advanced hobby projects.

KSP44 Pinout

Understanding the KSP44 Pinout Configuration
The KSP44 pinout follows a Collector–Base–Emitter (E-B-C) arrangement when viewed from the flat side of the TO-92 package. Correct pin identification is essential for proper circuit operation and to avoid component damage.
| Pin# | Pin Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter |
| 2 | Base |
| 3 | Collector |
KSP44 Key Features
- High voltage handling capability
- Stable switching and signal control performance
- Compact TO-92 package
- Suitable for low-current applications
- Easy integration into PCB layouts
- Reliable operation in continuous use
Characteristics / Specifications
- Transistor Type: NPN
- Package Type: TO-92
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE): 500V
- Collector-Base Voltage (VCB): 400V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (VEB): 6V
- Continuous Collector Current (IC): 300mA
- Power Dissipation (PD): 625mW
- Maximum Junction Temperature (Tj): 150°C
- Storage Temperature Range (Tstg): -55°C to 150°C
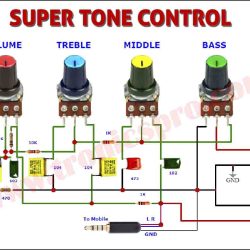
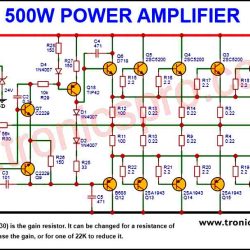
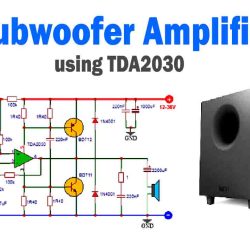
More Circuit Layouts
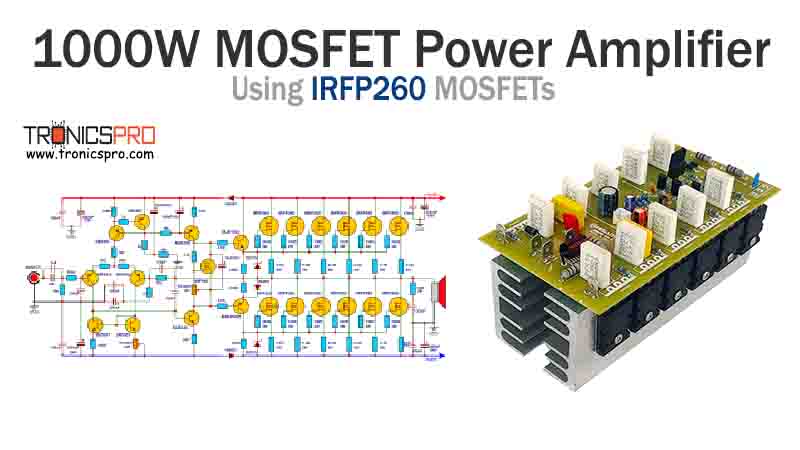
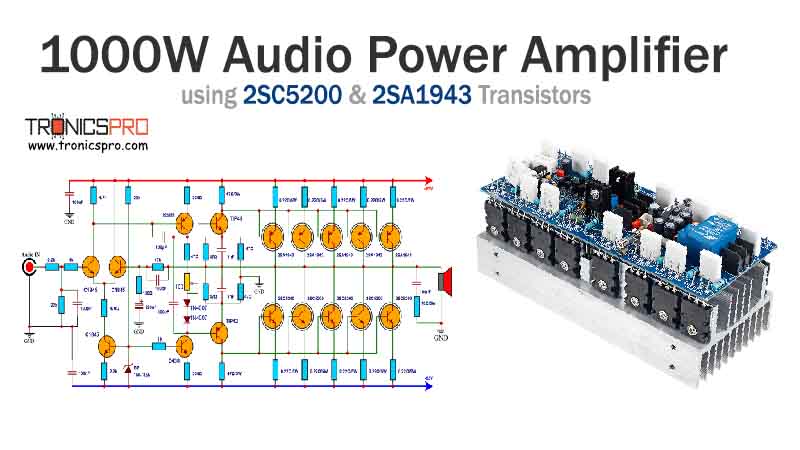
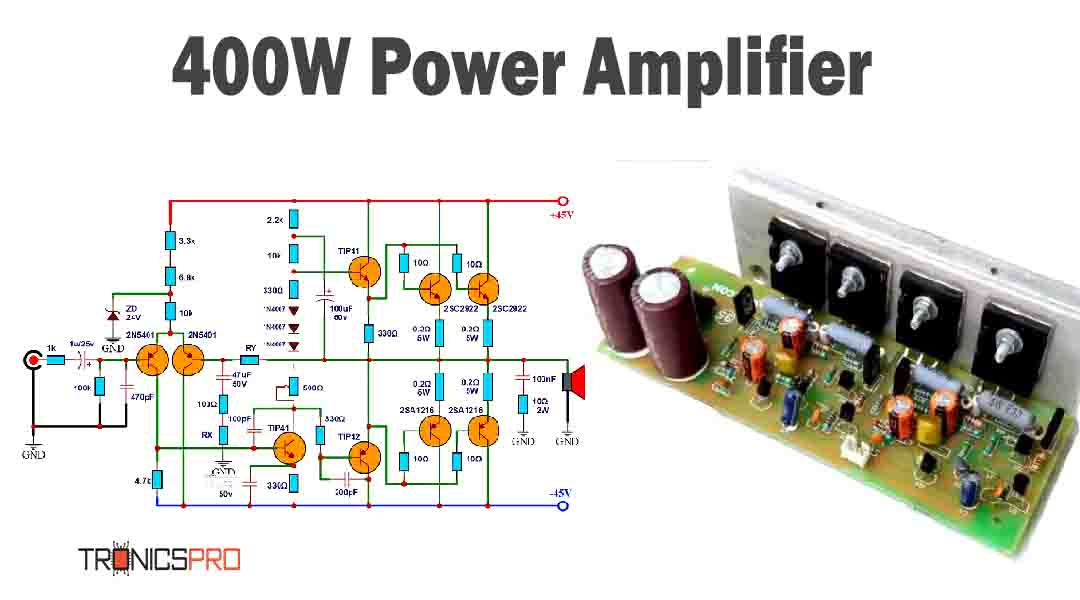
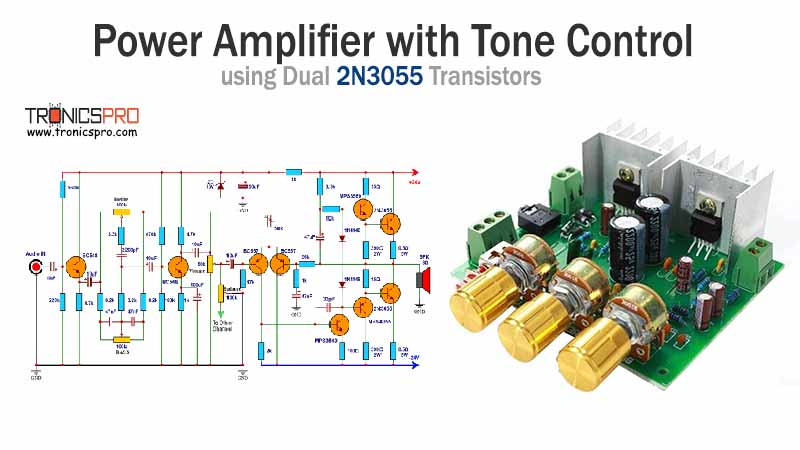

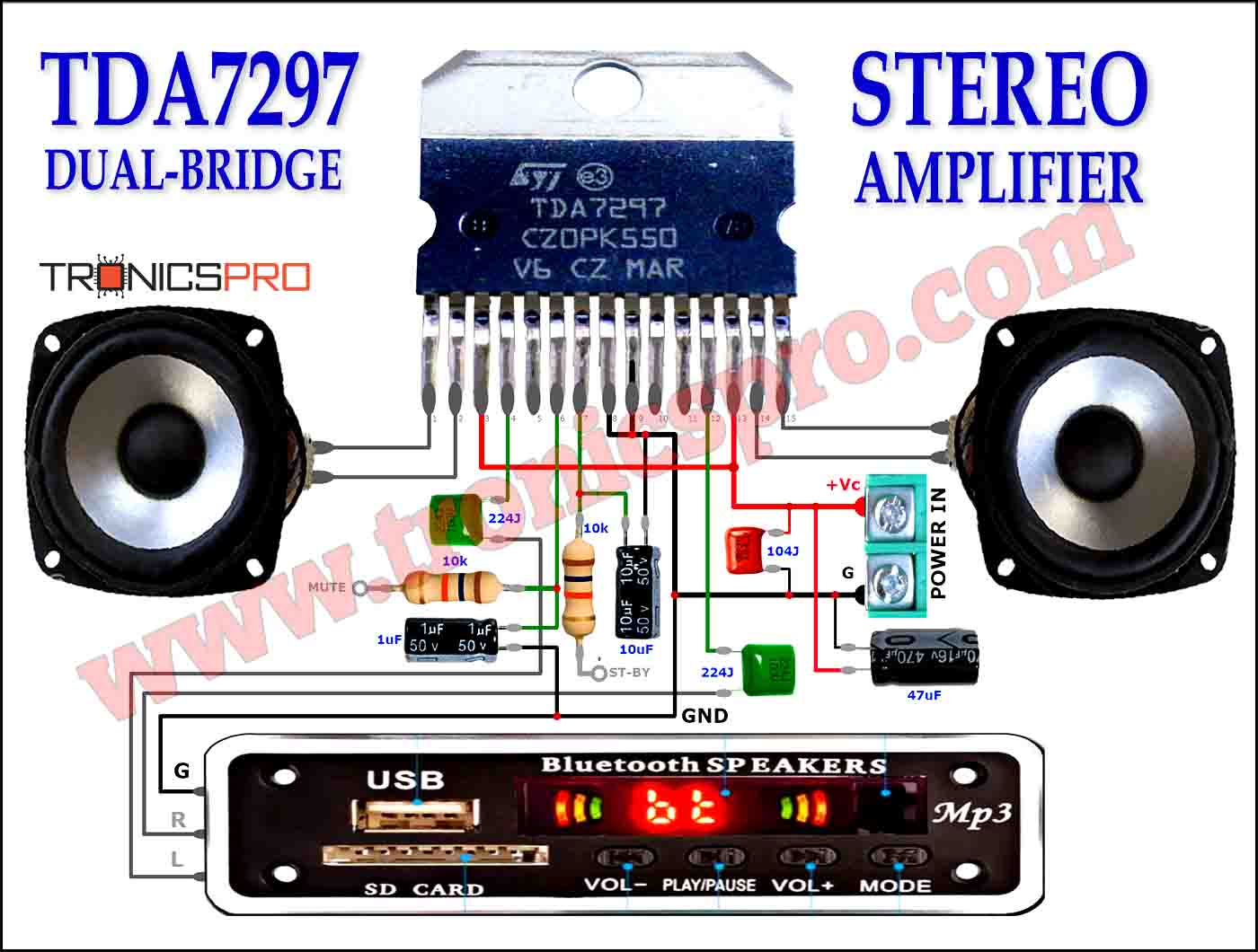

Key Applications of KSP44 NPN Transistor
- Display driver circuits
- High-voltage switching applications
- Signal control stages
- Power management circuits
- Industrial control electronics
- Consumer electronic equipment
Equivalent of KSP44 NPN Transistor
The following transistors can be considered as alternatives to the KSP44 with suitable design adjustments:
Working Principle of KSP44
The KSP44 operates as a bipolar junction transistor where a small base current controls a larger current flow between the collector and emitter. When the base-emitter junction is forward biased, charge carriers move through the device, enabling switching or signal control action.
This operating behavior makes the KSP44 suitable for high-voltage, low-current control and switching applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What package is used for the KSP44 transistor?
The KSP44 is available in a TO-92 package.
Q2: What is the KSP44 pinout order?
The pin configuration is Collector, Base, and Emitter (C-B-E).
Q3: Can KSP44 be used in high-voltage circuits?
Yes, it is specifically designed for high-voltage, low-current applications.
Q4: Is KSP44 suitable for display driver circuits?
Yes, it is commonly used in display and indicator driver stages.
Conclusion
The KSP44 NPN transistor is a dependable solution for high-voltage electronic applications that require stable signal control and compact design. With a clearly defined ksp44 pinout, consistent operating characteristics, and wide application range, it is well suited for switching and control tasks in modern electronic circuits.
Datasheet of KSP44 NPN Transistor
Click the following Button to download the datasheet of KSP44 Transistor :
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.