Before diving into the detailed sections, note the IRF840 pinout, it uses the standard TO-220 layout: Gate–Drain–Source (G-D-S). Understanding this pin mapping beforehand helps ensure correct installation in high-voltage SMPS circuits, inverter stages, motor drivers, and other applications where a wiring mistake can instantly damage the MOSFET due to the high voltages involved.

Introduction to IRF840 N-Channel MOSFET
The IRF840 is a high-voltage N-channel enhancement-mode power MOSFET widely used in SMPS primary stages, inverter circuits, offline power supplies, and high-voltage switching applications. It combines a 500 V drain-source rating with fast switching capability, making it a strong choice for designers working on AC mains–powered converters, high-voltage DC supplies, and other demanding power electronics. Its TO-220 body gives good thermal performance while maintaining cost-effectiveness and easy PCB integration.
IRF840 N-Channel MOSFET

Pinout of IRF840

Pin Configuration of IRF840 Pinout
The IRF840 pinout is based on the highly common TO-220 standard with three leads arranged as:
| Pin# | Pin Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Gate |
| 2 | Drain |
| 3 | Source |
The metal tab is also connected internally to the drain, so proper insulation is required if mounting it on a grounded heatsink.
Key Features of IRF840 MOSFET
- High-voltage capability suitable for AC mains applications
- Fast switching for SMPS and inverter topologies
- Strong avalanche energy handling
- Rugged TO-220 package for superior heat dissipation
- Easy gate drive requirements relative to bipolar devices
- Suitable for medium-power conversion and motor-control applications
Datasheet and Specifications of IRF840 MOSFET
- VDS (Drain-Source Voltage): 500 V
- VGS (Gate-Source Voltage): ±20 V
- ID (Continuous Drain Current): 8 A
- IDM (Pulsed Drain Current): 32 A
- RDS(on) (Drain-Source On-Resistance): 0.85 Ω
- Ptot (Total Power Dissipation): 125 W
- Tstg (Storage Temperature Range): −65°C to +150°C
- TJ (Junction Temperature): 150°C
- Package: TO-220
- Pin Configuration: G – D – S (front view)
Working Principle of IRF840 MOSFET
The IRF840 operates as a voltage-controlled switch. When a positive voltage is applied between the gate and source above the threshold level, an n-channel forms, enabling current to flow from drain to source. This makes the device ideal for PWM switching, on/off control, and high-voltage conversion. Its fast switching behavior reduces switching losses, improving efficiency in SMPS and inverter designs. However, the MOSFET must be driven with a proper gate voltage (typically around 10–12 V) to minimize conduction losses.
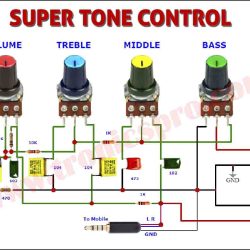
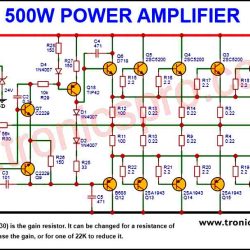
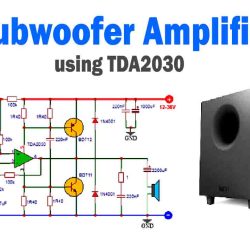
More Circuit Layouts
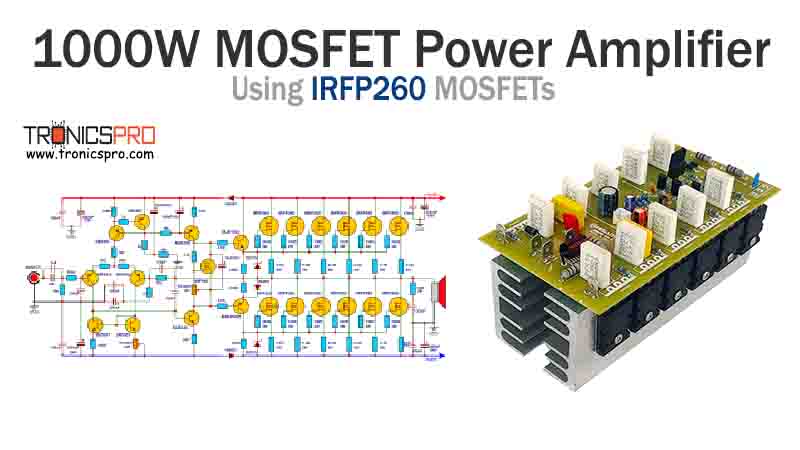
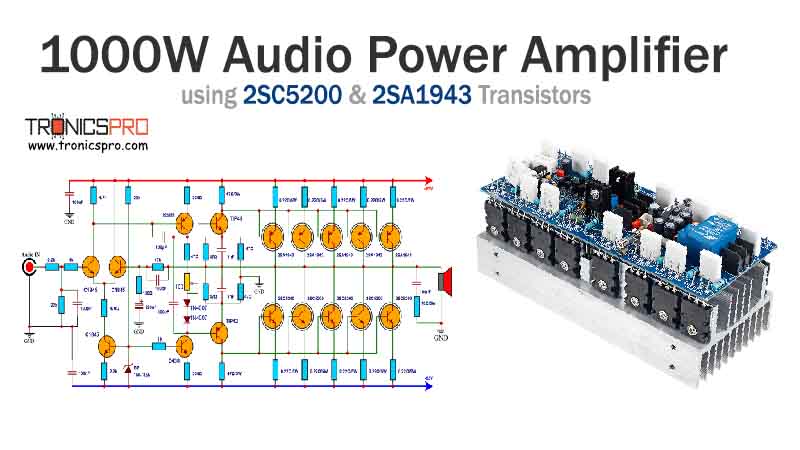
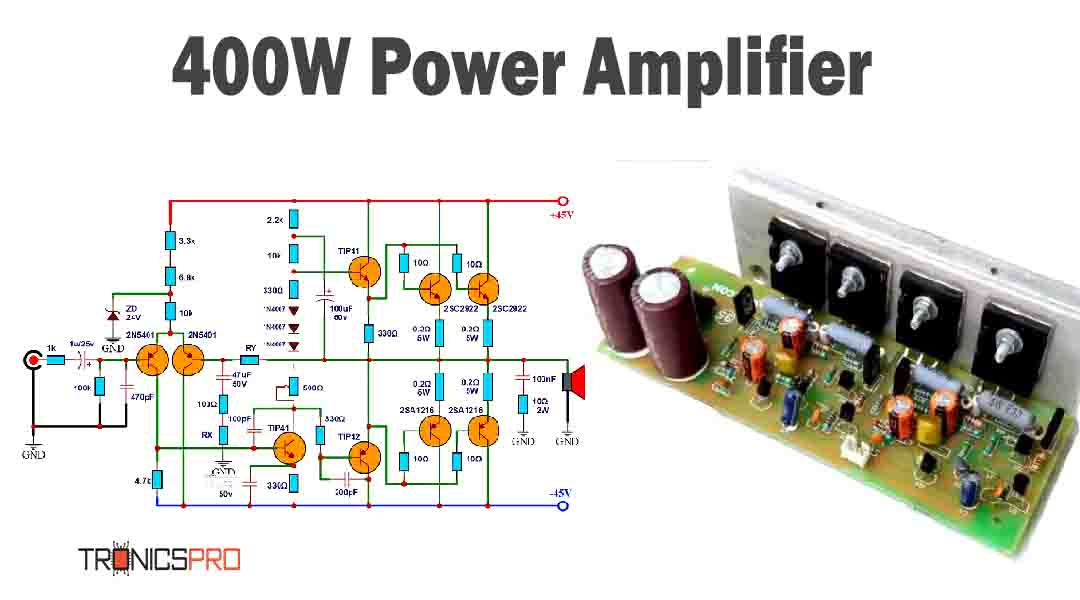
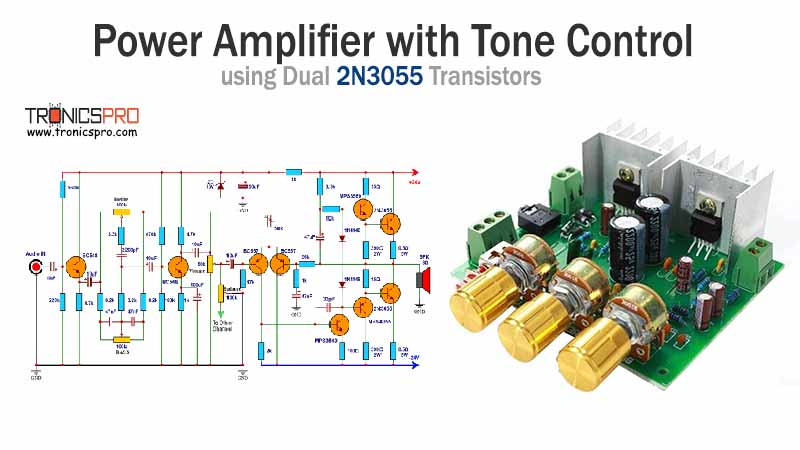

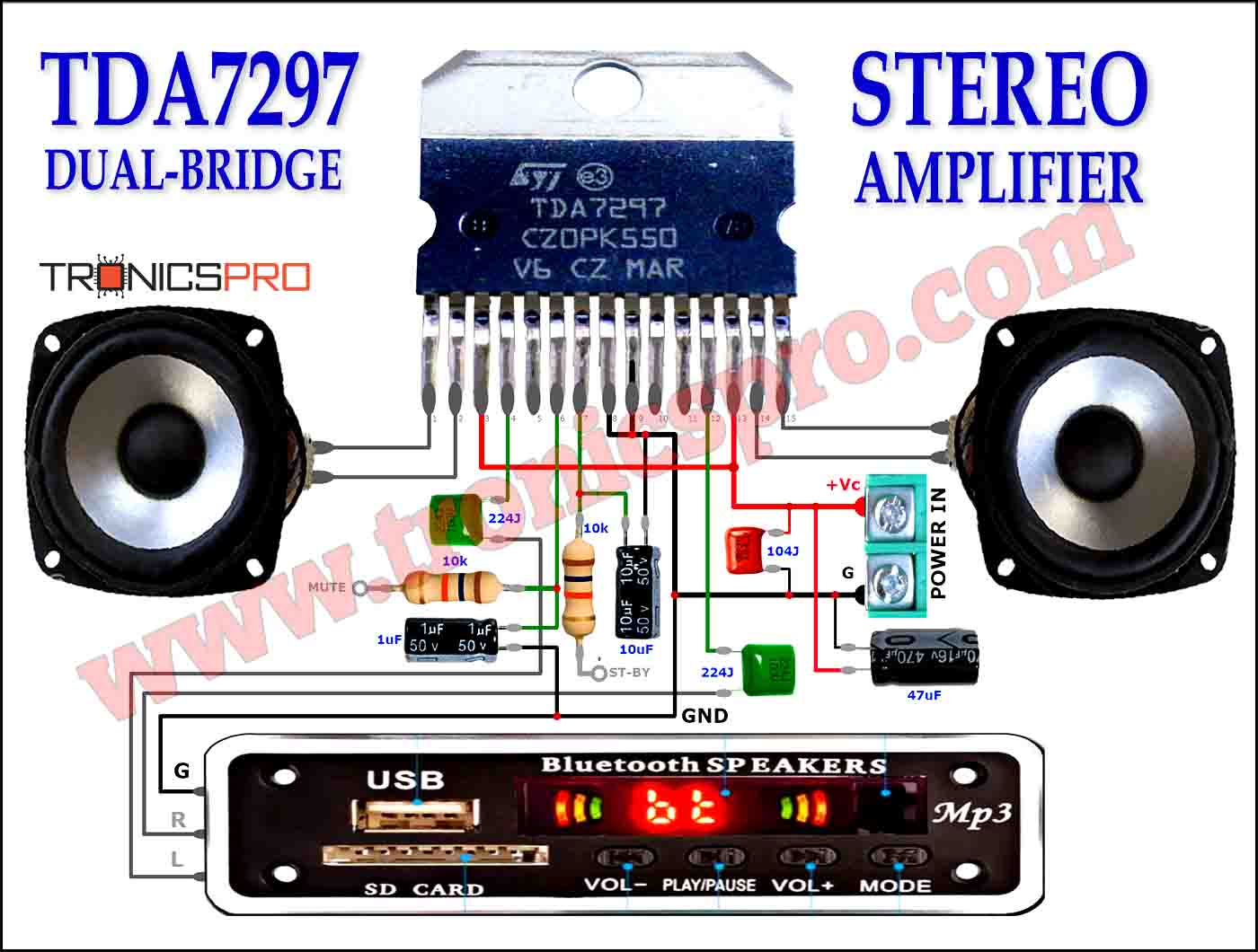

Applications of IRF840 MOSFET
- SMPS primary-side switching (flyback, forward converters)
- High-voltage inverters and DC–AC conversion
- LED drivers and lamp ballasts
- High-voltage DC power supplies
- Induction heaters and high-frequency drivers
- Motor control circuits (medium power)
- Battery chargers and offline AC-powered systems
Equivalent and Alternative MOSFETs
Suitable alternatives with similar ratings (verify datasheet before replacement):
- IRF740 (lower current, similar voltage)
- IRF830/IRF820 (lower current/voltage options depending on requirement)
- STF10N50, 2SK1119, or similar 500 V MOSFETs
- IRFP series for higher current demands (different package)
Always verify RDS(on), ID, and thermal limits before substituting.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the IRF840 pinout?
It follows Gate – Drain – Source (G-D-S) in TO-220, with the tab connected to the drain.
Q2: Can IRF840 run directly from microcontroller GPIO pins?
No. It requires a proper gate driver or at least a buffer to provide sufficient gate charge.
Q3: Is IRF840 suitable for high-frequency SMPS?
Yes, but at very high frequencies switching losses rise. For >100 kHz operation, use MOSFETs designed with lower gate charge.
Q4: Does IRF840 require a heatsink?
Yes — for medium to high power usage, heatsinking is mandatory due to its high dissipation capability.
Conclusion
The IRF840 is a robust and versatile high-voltage N-channel MOSFET ideal for SMPS, inverters, and high-voltage power control. Its 500 V capability, reliable switching performance, and TO-220 thermal characteristics make it a dependable choice for designers. Correct usage of the IRF840 pinout, proper gate drive, and adequate heatsinking ensures long-term and safe performance in demanding power electronics environments.
Datasheet & Pinout of IRF840 N-Channel MOSFET
Click the following Button to download the datasheet of IRF840 MOSFET :
More projects:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.