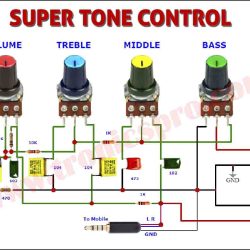
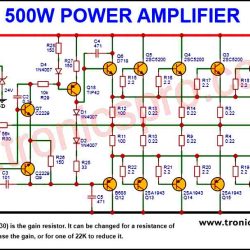
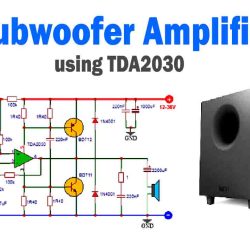
The BD540 PNP transistor is a high-power silicon transistor used for efficient amplification and power switching. Complementary to the BD539 NPN transistor, it offers balanced performance in push-pull amplifiers and voltage regulator circuits. In this post, you’ll find the complete BD540 pinout, transistor datasheet, equivalents, and applications, along with specifications and circuit insights for optimal design performance.
Introduction to BD540 PNP Transistor
The BD540 PNP transistor is a high-performance silicon transistor designed for power amplification and switching applications. It serves as the complementary PNP pair to the BD539 NPN transistor, forming a balanced and efficient combination for push-pull amplifier circuits, voltage regulators, and motor drivers.
With a collector current (Ic) of up to 4 amperes and a collector-emitter voltage (Vce) rating of 100 volts, the BD540 transistor provides strong current control and excellent reliability in medium to high-power circuits. It features a durable TO-220 package, ensuring efficient thermal dissipation, which is crucial for stable operation under heavy load conditions.
Because of its excellent current gain characteristics, wide safe operating area, and low saturation voltage, the BD540 transistor is frequently used in audio output stages, switching regulators, and DC power control systems. Engineers and hobbyists appreciate its compatibility with NPN counterpart BD539, which makes it ideal for symmetrical amplifier designs and high-efficiency power circuits.
BD540 PNP Transistor

Pinout of BD540
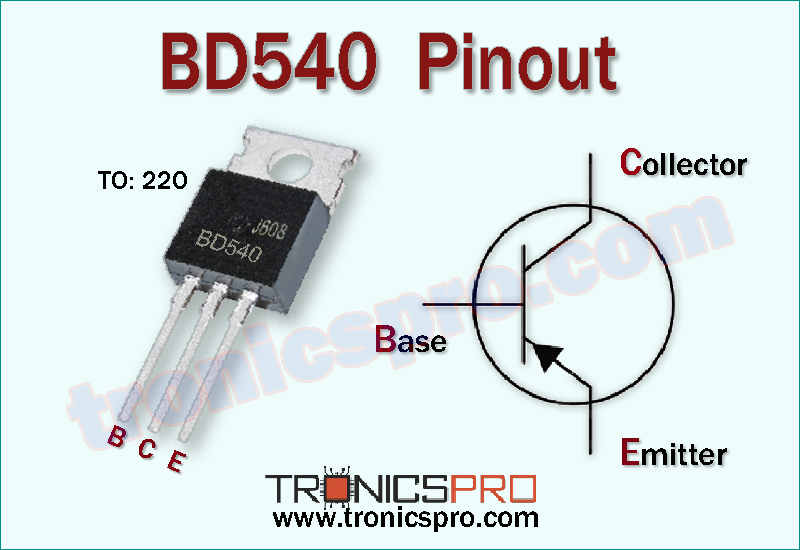
Understanding the BD540 Pinout Configuration
The BD540 pinout defines the transistor’s connectivity for circuit implementation. Like other transistors in the BD series, it follows a TO-220 package layout, ensuring consistent mounting and wiring orientation in amplifiers and power boards.
When facing the flat side with the leads downward, the pin configuration for BD540 is:
Pin 1 – Base (B), Pin 2 – Collector (C), and Pin 3 – Emitter (E).
Understanding the BD540 pin configuration helps avoid wiring mistakes and ensures optimal biasing in complementary circuits with BD539. This configuration is critical for precise control in audio and power output stages.
Pin Configuration of BD540 Pinout
| Pin# | Pin Name | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Base | Controls transistor bias |
| 2 | Collector | Connected to load/output |
| 3 | Emitter | Current flow terminal |
Key Features of BD540 Transistor
- PNP silicon power transistor for amplification and switching
- High collector current handling capacity up to 4A
- Low saturation voltage for efficient switching
- Excellent linear gain and frequency response
- Reliable performance in TO-220 package
- Complementary to BD539 NPN transistor
- Suitable for medium to high-power applications
BD540 Transistor Datasheet and Specifications
The BD540 transistor datasheet outlines its electrical characteristics and maximum ratings for safe and efficient use in power circuits. The key specifications include:
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vceo): 100V
- Collector-Base Voltage (Vcbo): 100V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (Vebo): 5V
- Collector Current (Ic): 4A
- Power Dissipation (Ptot): 40W at 25°C
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 to 160 (varies with Ic)
- Transition Frequency (fT): 3 MHz typical
- Operating Junction Temperature: -65°C to +150°C
- Package Type: TO-220
These ratings ensure that the BD540 can handle demanding conditions in audio amplifiers, motor drivers, and switching regulators with minimal signal distortion and excellent thermal performance.
Working Principle of BD540 PNP Transistor
The BD540 PNP transistor functions as a current-controlled device that allows current to flow from emitter to collector when a small current is applied at its base terminal (in reverse polarity compared to NPN types).
In simple terms, when the base is made negative relative to the emitter, the transistor turns on, allowing current to pass through the collector. This operation is opposite to its NPN counterpart BD539, which requires a positive base bias.
This characteristic makes the BD540 transistor ideal for complementary push-pull amplifier stages, where it handles the negative half of the signal waveform, while BD539 handles the positive half. This results in more balanced output power and reduced crossover distortion.
More Circuit Layouts
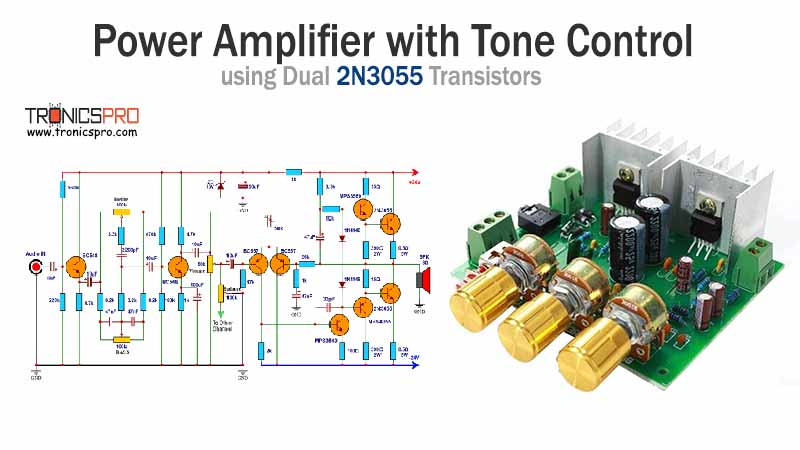

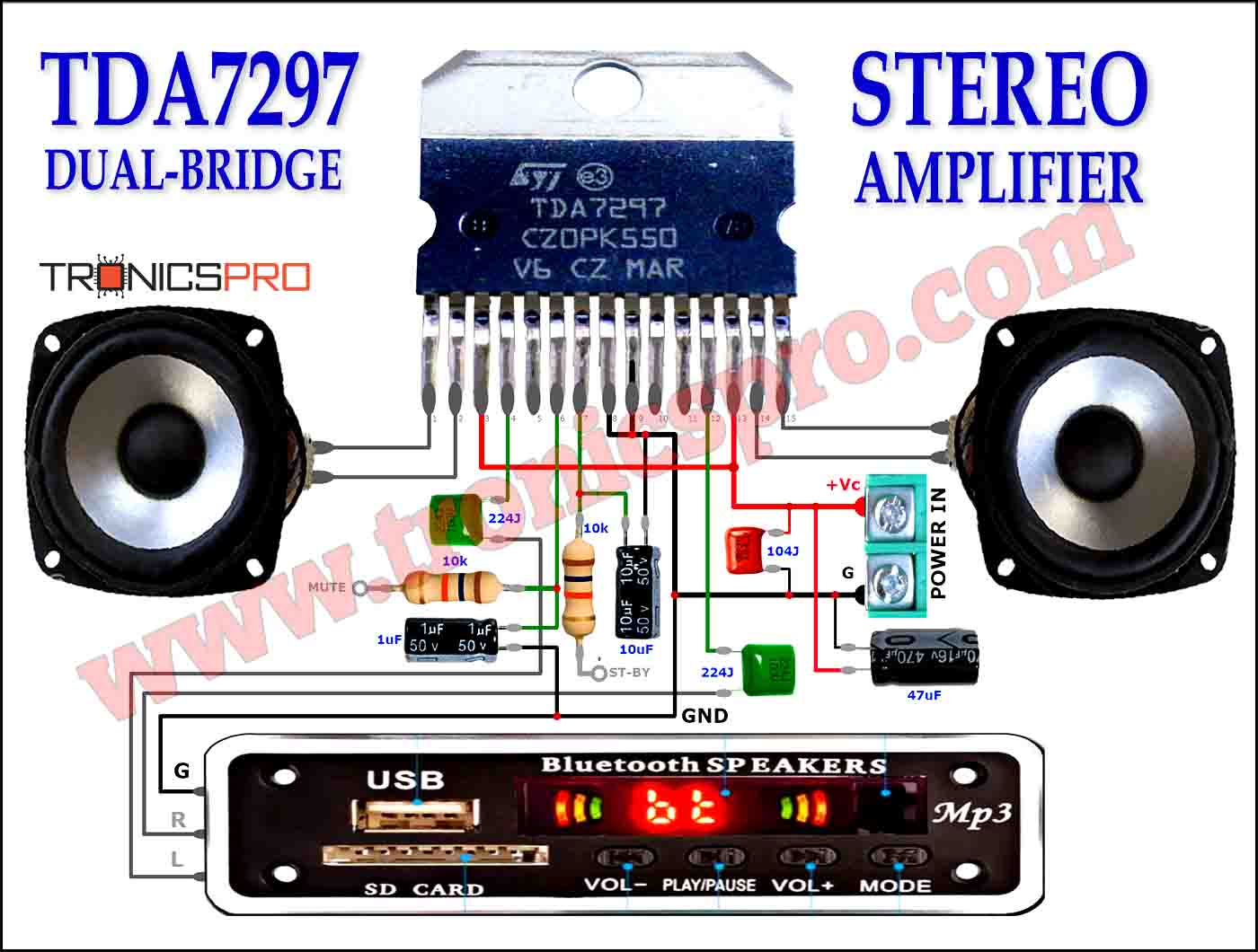

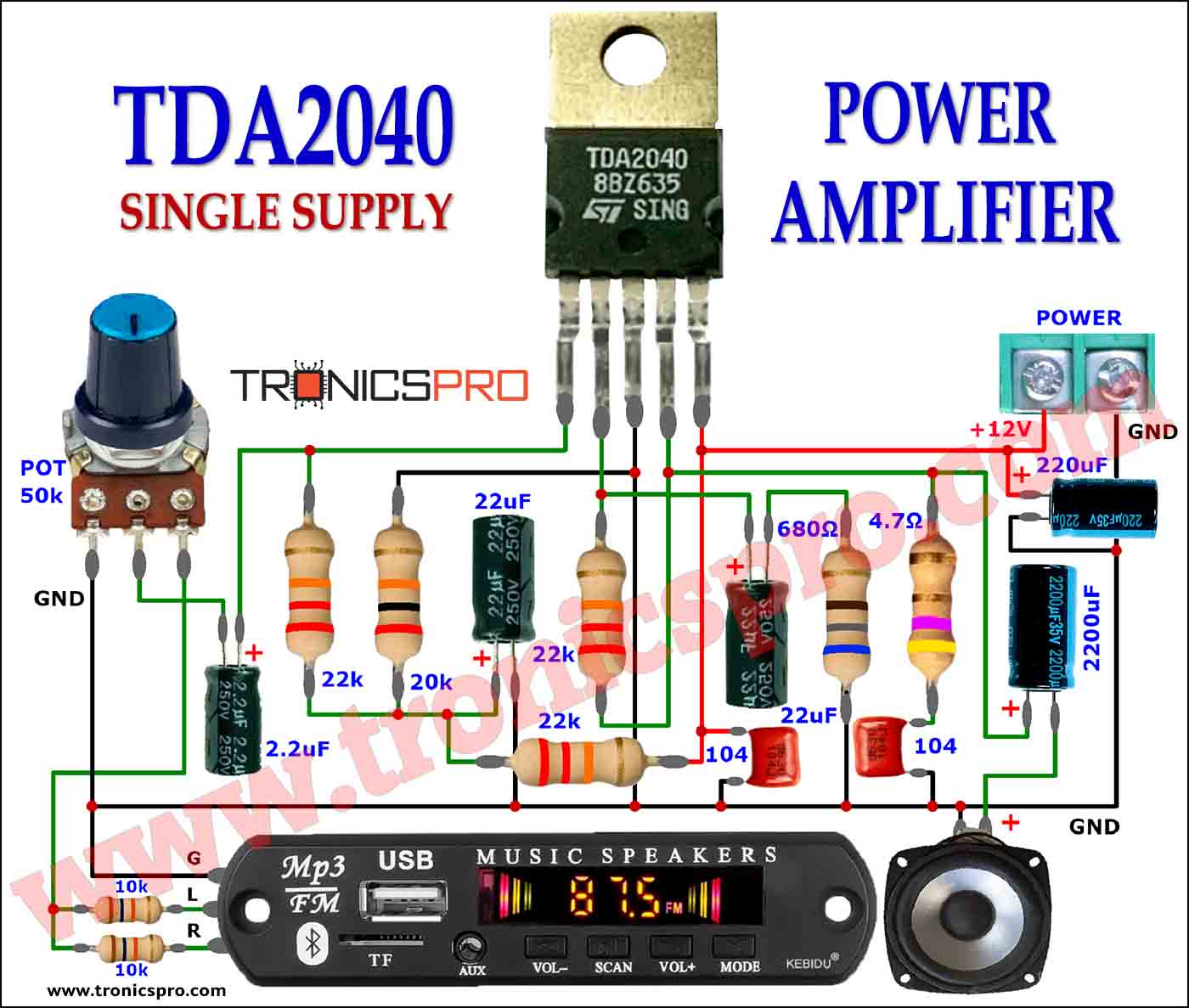
Typical Applications of BD540
The BD540 PNP transistor is used in a wide range of power and signal applications where efficiency and balance are important. Common applications include:
- Audio amplifier output stages
- Power driver and control circuits
- Motor driver systems
- Switching regulators and voltage stabilizers
- Inverter circuits and converters
- Relay and solenoid drivers
- Push-pull amplifier configurations
Its compatibility with BD539 NPN transistor allows for seamless integration in dual-transistor or complementary power amplifier setups that demand stable and distortion-free performance.
NPN Complementary Transistor
The NPN complementary transistor for BD540 is the BD539 transistor. Both transistors share identical voltage, current, and gain characteristics but operate with opposite polarities.
When used together in push-pull amplifier configurations, BD539 conducts the positive waveform, and BD540 handles the negative waveform, ensuring a continuous and balanced signal output. This combination minimizes signal distortion and improves amplifier efficiency.
The complementary pairing of BD539 NPN transistor and BD540 PNP transistor is widely used in audio amplifiers, motor control systems, and switching circuits that require symmetrical performance and stable output power.
Equivalent Transistors and Alternatives
If the BD540 transistor is not available, several equivalent or substitute transistors can be used in its place depending on circuit requirements:
- BD536 – Similar voltage and current ratings with PNP polarity
- BD244C – Suitable for power amplification and switching
- TIP32C – General-purpose PNP transistor with comparable ratings
- 2N2955 – Classic PNP power transistor for heavy-duty applications
- BD238 – Alternative PNP device for medium-power circuits
Before substitution, always confirm the pin configuration and maximum ratings to ensure compatibility and safe circuit operation.
Comparison BD540 vs BD539 Complementary Transistors
The BD540 (PNP) and BD539 (NPN) transistors are complementary devices that work in perfect opposition to deliver high-performance signal amplification and power control.
While the BD539 NPN transistor conducts when the base is positively biased, the BD540 PNP transistor conducts when the base is negatively biased. This opposite behavior allows them to share the current load efficiently in push-pull amplifiers, ensuring smooth and balanced audio reproduction.
Both transistors feature similar ratings—100V maximum collector-emitter voltage, 4A collector current, and identical power dissipation—making them interchangeable in complementary design setups. The BD540 handles the negative phase, while the BD539 handles the positive phase, resulting in a more efficient and distortion-free signal flow.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the BD540 transistor used for?
The BD540 transistor is used in audio amplifiers, voltage regulators, and power switching circuits that require moderate to high current handling.
What type of transistor is BD540?
The BD540 is a PNP silicon power transistor designed for amplification and high-power switching.
What is the BD540 pin configuration?
The BD540 transistor has a TO-220 package with Pin 1 – Base, Pin 2 – Collector, Pin 3 – Emitter.
What is the complementary transistor for BD540?
The complementary NPN transistor for BD540 is the BD539, which has identical electrical ratings but opposite polarity.
Can I use BD238 instead of BD540?
Not recommended. The BD238 is a lower-power transistor with different voltage and current ratings, making it unsuitable for circuits designed for BD540.
Conclusion
The BD540 PNP transistor is a highly efficient and reliable component for audio, power, and switching circuits. Its excellent gain stability, thermal performance, and compatibility with the BD539 NPN transistor make it a top choice for engineers building balanced and distortion-free amplifiers.
Understanding the BD540 pinout, datasheet values, and equivalents helps in proper circuit integration and ensures long-term performance. When paired with the BD539, the BD540 transistor contributes to efficient and high-fidelity power amplification in both consumer and industrial applications.
Datasheet of BD540 NPN Transistor
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.