The BD238 PNP transistor is a popular power device widely used in amplifier and switching applications. It is designed for medium-power output stages and low-frequency linear amplifiers, making it a trusted choice for both hobbyists and professionals. This article provides a complete guide to the BD238 pinout, BD238 datasheet, equivalents, and applications, everything you need to know to use it efficiently in your electronic projects.
Introduction to BD238 PNP Transistor
The BD238 transistor is a silicon-based PNP bipolar junction transistor (BJT) that can handle moderate voltage and current levels. It belongs to the BD23x transistor family, which includes complementary and similar types such as BD237 (NPN) and BD239 (NPN high power).
This transistor is primarily used for audio amplifier circuits, switching regulators, and medium-power signal processing. With a collector current of up to 2A and a collector-emitter voltage of up to 80V, the BD238 offers reliable performance for various analog and digital applications.
The BD238 pinout and configuration make it easy to integrate into circuit designs, especially in class AB amplifiers, driver stages, and low-frequency power control modules.
BD238 PNP Transistor

Pinout of BD238
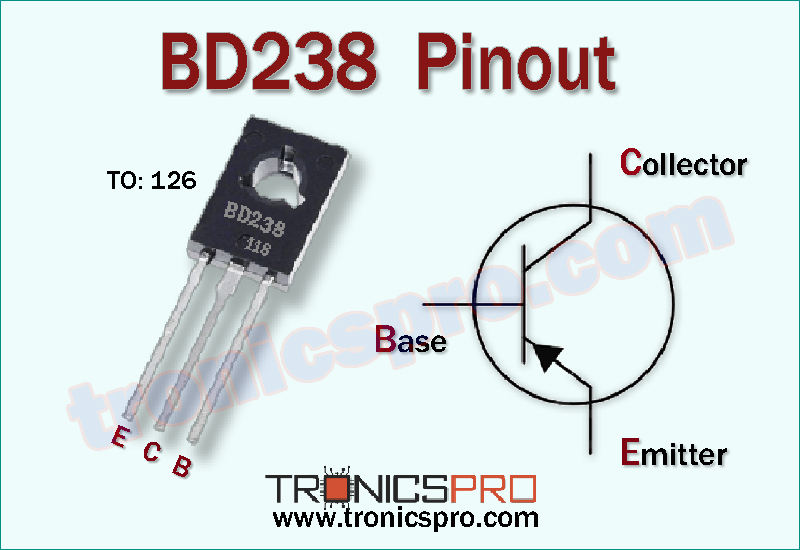
Understanding the BD238 Pinout Configuration
The BD238 pin configuration consists of three terminals — Emitter (E), Collector (C), and Base (B). These pins are arranged in the TO-126 package, which allows good heat dissipation and compact installation on heat sinks.
Pin Configuration of BD238 Pinout
| Pin# | Pin Name | Pin Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Emitter | Current flows out through this terminal |
| 2 | Collector | Connected to the load or supply voltage |
| 3 | Base | Controls the transistor switching or amplification |
Understanding the BD238 pinout is crucial for proper circuit connections. Reversing collector and emitter terminals can lead to failure or reduced performance. Always verify the BD238 datasheet before connecting the transistor.
Key Features of BD238 Transistor
- Medium power handling capability
- Suitable for audio frequency amplifiers
- Designed for low-frequency linear applications
- High collector current tolerance
- Reliable thermal stability in TO-126 package
- Complementary with BD237 (NPN)
- Easy replacement for general-purpose PNP transistors
BD238 Transistor Datasheet and Specifications
Below are the confirmed specifications from the BD238 datasheet that define its electrical and thermal performance:
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (Vceo): 80V
- Collector-Base Voltage (Vcbo): 100V
- Emitter-Base Voltage (Vebo): 5V
- Collector Current (Ic): 2A continuous
- Collector Dissipation (Pc): 25W maximum
- DC Current Gain (hFE): 40 to 250 depending on operating conditions
- Transition Frequency (fT): 3 MHz typical
- Operating Junction Temperature (Tj): up to 150°C
- Package Type: TO-126 plastic package
These specifications indicate that the BD238 can deliver consistent performance in medium power amplification, relay drivers, and switching regulators. It can safely handle high temperatures, making it suitable for continuous operation in compact electronic systems.
Working Principle of BD238 PNP Transistor
The BD238 PNP transistor conducts when a small negative current is applied to its base relative to the emitter. In the active region, it amplifies input signals, while in saturation, it behaves as a closed switch.
When the base-emitter junction is forward biased (around −0.7V), the transistor allows a large current to flow from emitter to collector. This property makes the BD238 ideal for both analog amplification and digital switching.
In power amplifier circuits, BD238 is commonly used as a driver transistor to push higher current loads. It works efficiently in push-pull amplifier stages when paired with its NPN counterpart (BD237 or BD239).
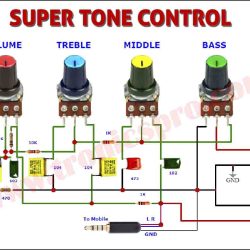
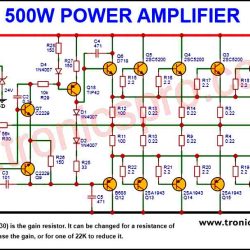
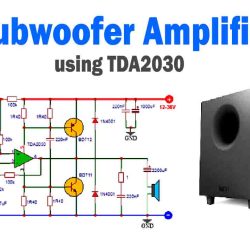
More Circuit Layouts
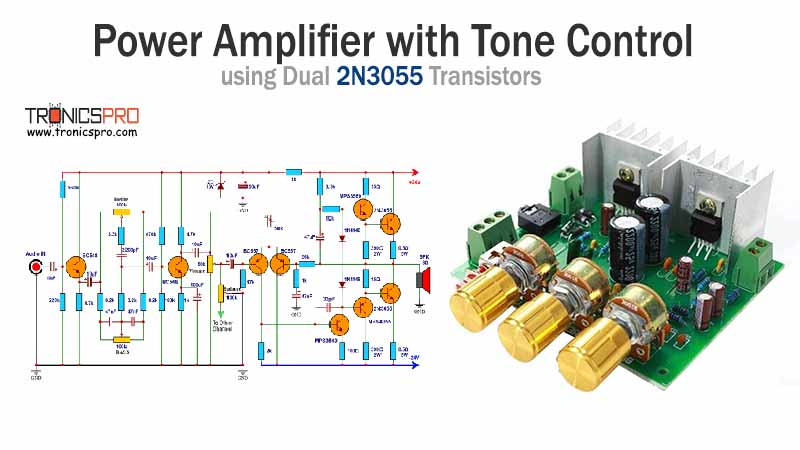

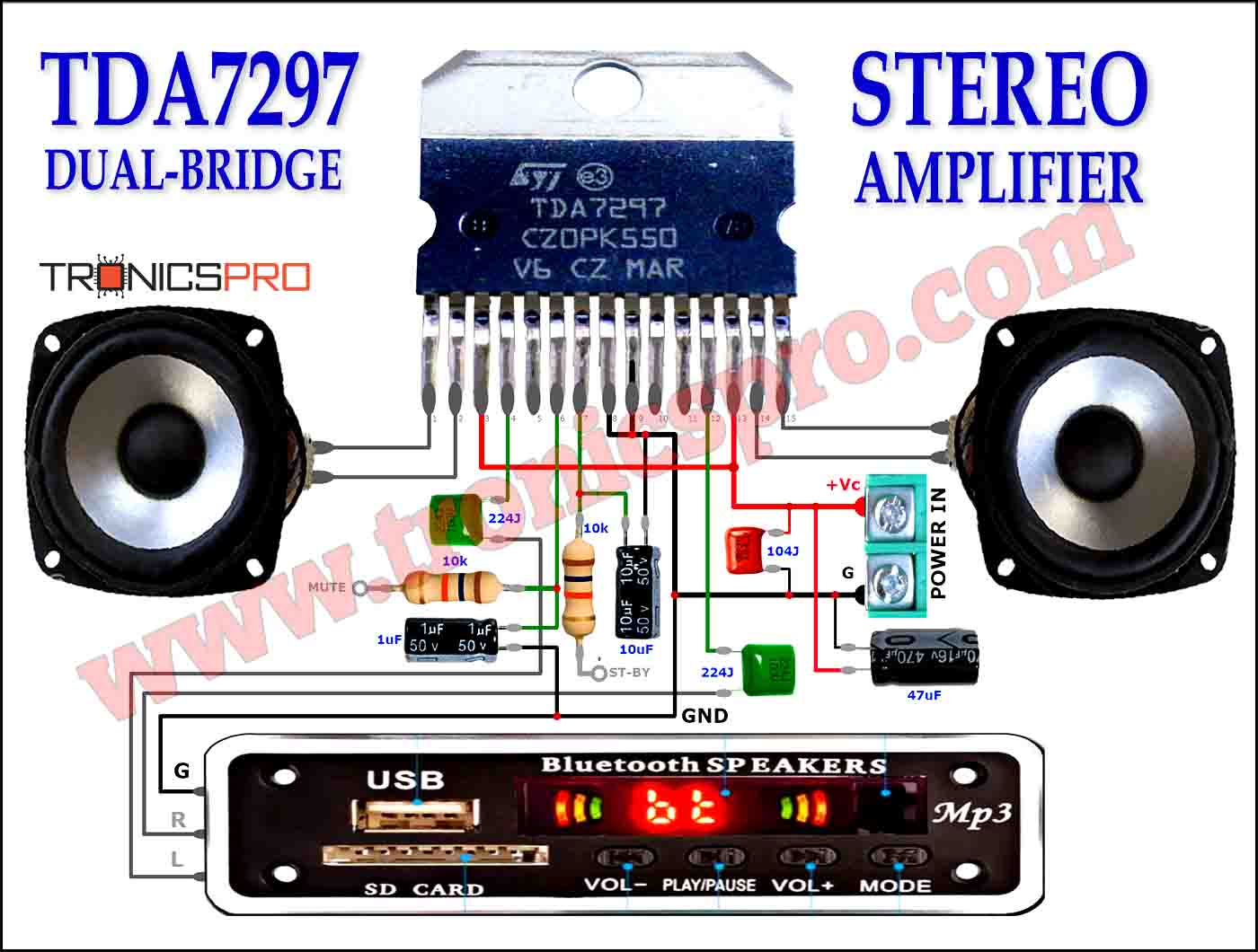

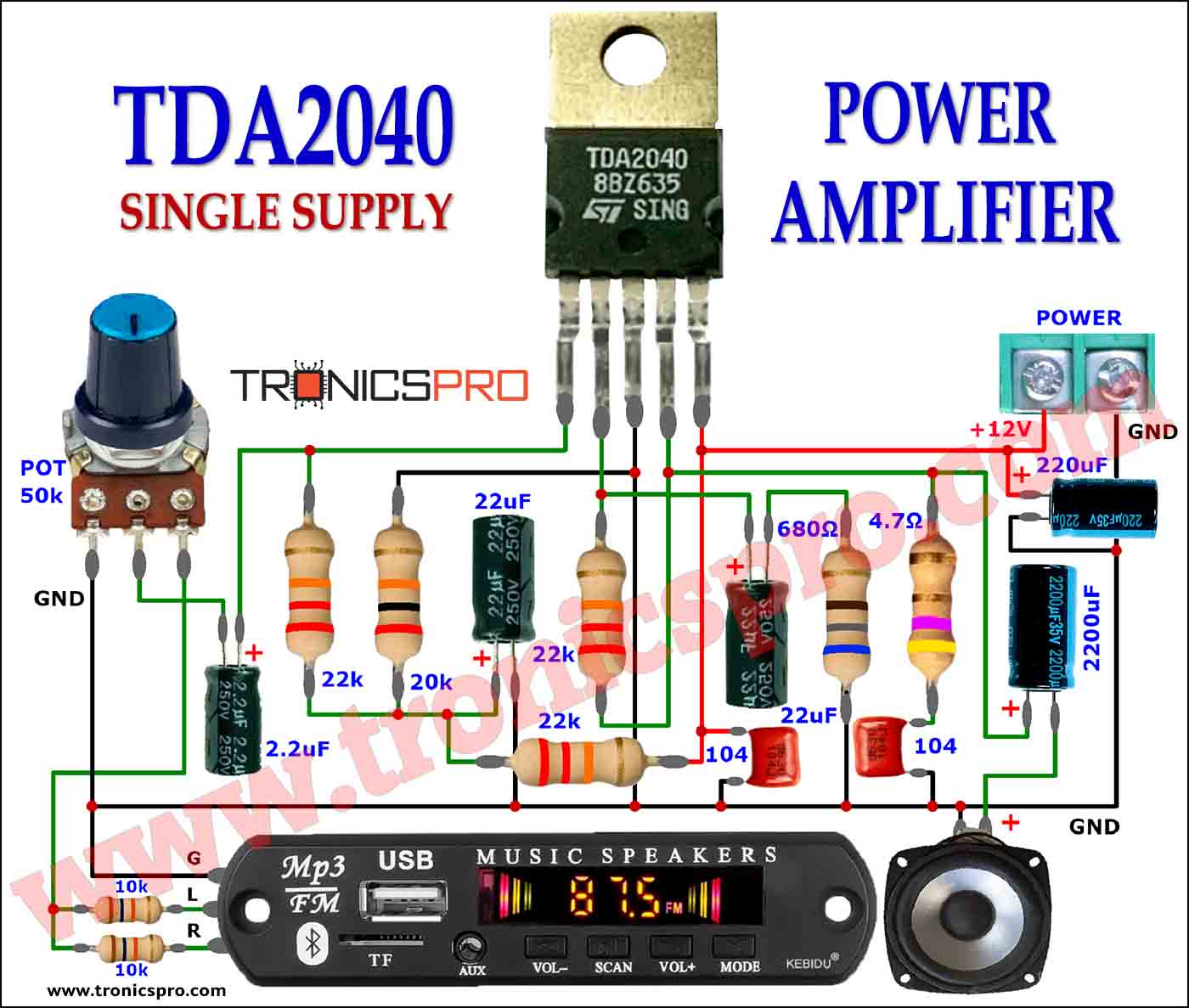
Typical Applications of BD238
- Audio amplifier driver and output stages
- DC motor and relay control circuits
- Power regulators and voltage controllers
- LED drivers and signal amplifiers
- Switching circuits and pulse control systems
- Low-frequency oscillators and waveform generators
- Complementary pair configurations with NPN transistors
NPN Complementary Transistor
The NPN complementary transistor for BD238 is the BD237. Together, BD237 (NPN) and BD238 (PNP) form a complementary pair often used in push-pull amplifier circuits, audio drivers, and DC switching systems.
Using complementary pairs allows designers to create efficient symmetrical amplifier stages with better thermal balance and distortion control.
Equivalent Transistors and Alternatives
The BD238 can be replaced by several other PNP power transistors with similar voltage and current ratings. Common equivalents include:
Always verify the pin configuration and maximum ratings before substitution to prevent circuit mismatches.
Comparison Summary of BD234 vs BD236 vs BD238 PNP
The BD234, BD236, and BD238 are from the same PNP transistor family, differing mainly in voltage and power ratings.
BD234 supports lower collector-emitter voltage (around 45V), making it suitable for small signal amplification. BD236 improves upon this with a higher voltage rating (around 60V) and better current handling, ideal for moderate load switching.
BD238, however, offers the best balance of voltage (80V) and current (2A) with higher gain and durability, making it the most versatile for audio amplifier outputs, regulators, and driver circuits.
Thus, among the three, BD238 provides the highest performance for high-voltage, medium-current applications while maintaining stability and low distortion.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the BD238 transistor used for?
The BD238 is mainly used in audio amplifier circuits, power regulators, and switching drivers for controlling medium-power loads.
What type of transistor is BD238?
It is a PNP bipolar junction transistor designed for low to medium-power amplification and switching applications.
What is the BD238 pin configuration?
From left to right (flat face facing you), the pins are Emitter, Collector, and Base.
What is the complementary transistor for BD238?
The NPN complementary transistor of BD238 is BD237.
Can I use BD238 instead of BD234?
Yes, BD238 can replace BD234 if the circuit operates within BD238’s voltage and current limits. However, check the biasing requirements before substitution.
Conclusion
The BD238 PNP transistor is a reliable and efficient medium-power device ideal for both analog and switching applications. With an 80V collector-emitter voltage, 2A current capacity, and TO-126 package, it offers excellent thermal stability and electrical performance.
Whether you are designing audio amplifiers, voltage regulators, or relay control systems, the BD238 provides the balance of durability, power, and cost-effectiveness you need. For best performance, always pair it with its NPN complement BD237 for push-pull or class AB configurations.
Datasheet of BD238 PNP Transistor
More projects, You may like:
- Video Transmitter DIY Homemade FM Radio Transmitter
- Adjustable Power Supply DIY Battery Charger
- 12V-220V 500 Watt inverter DIY Homemade
- MPPT Solar Charge Controller DIY Homemade
- DIY LA4440 bass amplifier homemade
For more project and circuit diagrams, you can go through the Schematics in the main menu where you can find many interesting projects and circuit diagrams like audio amplifier circuits, voltage booster circuit, battery charger circuit and timer circuits etc., which are all beginner circuit projects. Feel free to check them out!

Thank you for visiting the article.